Addressing the urban challenge
Breadth of the issue – How are the problem(s) that are being tackled by your initiative affecting citizens/local businesses or a significant component of the local wildlife?
DMSat1 was designed with the latest technologies to collect environmental data, serving as an important tool to drive environmental observations, to formulate strategies and key actions towards the protection of natural ecosystems, and to support a sustainable and resilient future for the emirate of Dubai. The project, therefore, utilizes the satellite’s capabilities to study and investigate Dubai’s environmental quality, including quality air and green cover, with the ultimate objective to maintain a sustainable living and healthy natural ecosystems capable of delivering the best benefits. For instance, DMSat1 utilizes Remote Sensing and Geographic Information system (GIS) to identify, locate and assess the quality and quantity of green cover as standardized by the World Health Organization (WHO) aimed at healthy living. The project, additionally, supports the development of air quality models to allow further investigations and relationships between the green cover and air pollution. This is made possible through the use of medium spatial resolution, and multi-spectral imagery as input for segmentation and object-based analysis and by adopting machine learning techniques to classify and extract green areas. These are subsequently compared to the DMSat1 air quality maps, such as Particulate Matter (PM 2.5, and PM10), NO2 and SO2, as well as the population density maps. This project is significant as it provides a wide range of benefits to the Emirate including.
- identification of the impacted areas or hot spots.
- identification of green cover and its quality.
- improving air quality for a healthy living and a healthy ecosystem.
Depth of the issue – How seriously are the problems being tackled by your initiative impacting the life of the citizens/businesses/wildlife concerned?
DMSat1 is ideal for observing the global environment as it is capable of revealing and monitoring environmental factors, their drivers of change and impacts, and providing valuable inputs to promote more environmentally sustainable development with significant contribution to many of the UN-SDG priorities, Paris Climate Agreement and the C40 organization. The DMSat1 delivers multiple interrelated benefits. For instance, utilizing the data generated by the project in conducting air quality pollution investigations and in developing air quality pollution maps (i.e. Particulate Matter (PM 2.5, and PM10, NO2 and SO2) provides the community with a variety of benefits including; identifying and addressing air quality stresses, and allowing the implementation of certain policies to limit and control air pollutants emissions. But also, and not less important, the scale of the benefits extends to serve the plants and vegetation, by determining the impacts and damage of air pollution on crops and trees. For example, ground-level ozone, a secondary pollutant formulated by a chemical reaction of NOX, VOC, and sunlight, can lead to the reduction in agricultural crop and commercial forest yields, reduced growth and survivability of tree seedlings, and increased plant susceptibility to disease, pests, and other environmental stresses. Unfortunately, the mangroves, an important ecosystem, could be among those impacted plants. Considering its importance in carbon sequestration and climate change impact protection, maintaining a healthy air environment is a priority. As such, the DMSat1 is a critical tool and a source of information to achieve a resilient and sustainable future of the Dubai city.
The power of plants and natural ecosystems to deliver benefits
How is the initiative shaped by scientific evidence of the potential for plants and natural ecosystems to deliver benefits?
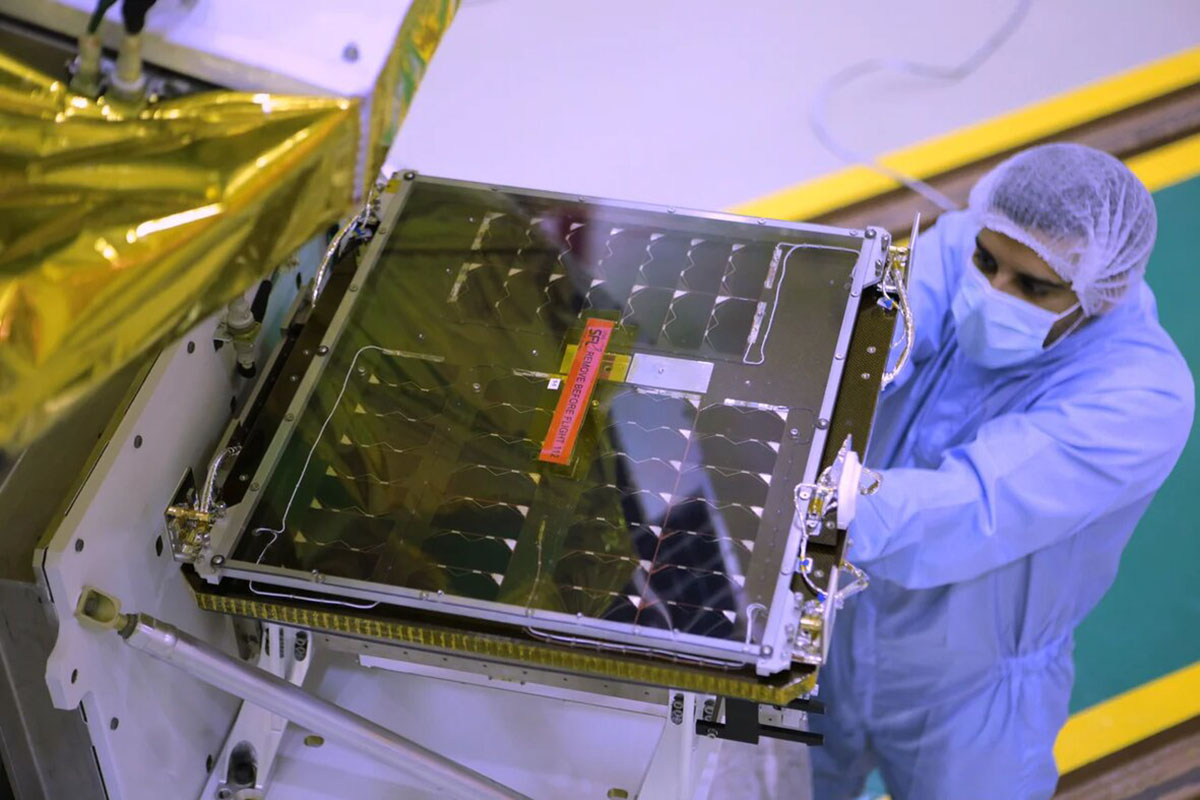
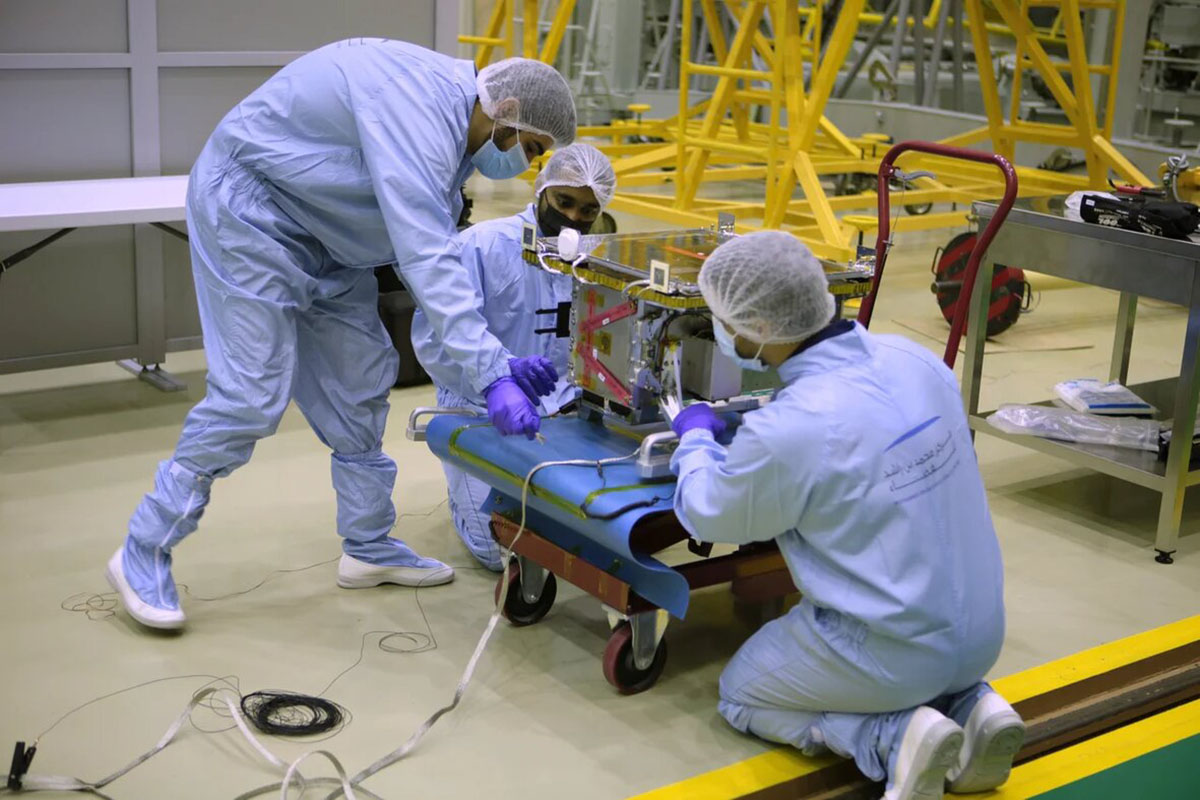
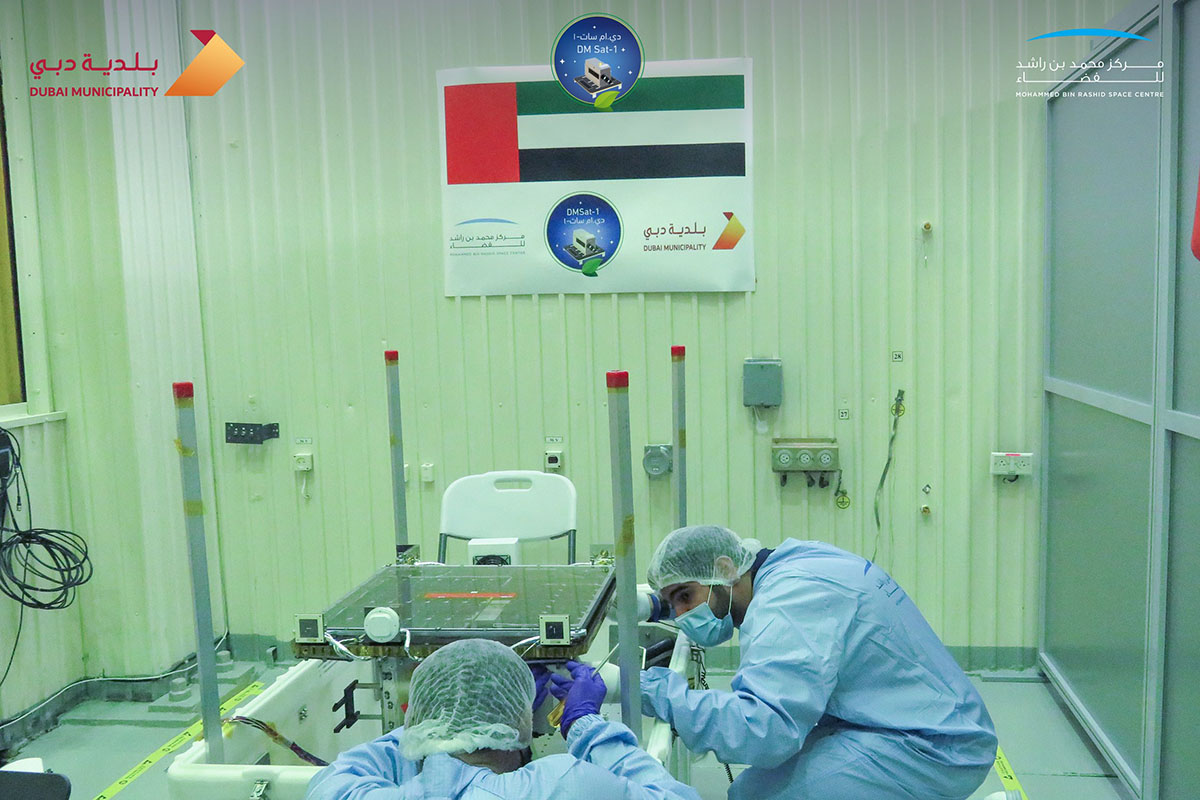
The DMSat1 was designed innovatively as a high-performance nanosatellite, having the world’s up-to-date environmental space monitoring technologies to perform multi-spectral observations, critical altitude control, and precise sensor pointing. It is characterized by its lightweight, being just over 15 kg, and its compact dimensions along with several distinctive features of the next generation of satellites, including the ability to orbit the Earth 14 times a day with a revisit rate of 3 to 5 days. It is equipped with multispectral remote sensing cameras and orbits at an altitude of 730 kilometres above the Earth’s surface. The DMSat1 is powered by solar storage panels capable of generating power greater than 36 W, and is complemented by keep-alive solar arrays on all faces to enable power generation at any altitude.
How has the city exploited the potential of plants and associated ecosystems to deliver more than one benefit?
The DMSat1 project was envisaged as a collaborative venture following rigorous development processes. The project is supported by highly qualified engineers, GIS specialists, city planners and environmental scientists during the planning, design and manufacturing phases, and during the launch of the nanosatellite and subsequent data collections/analysis. Significant collaborative work is initiated with the research academic facilities with the ultimate objective to support and drive the scientific research in the environmental fields, and develop new research areas of interest in human health and impacts of air pollution. This will consequently, enable collaborative opportunities with the heath sector and support the development of health strategic plans in promoting healthy community living.
Innovative and Collaborative Solution
How does the initiative show evidence of feasibility, including on-going financial and logistical support?
Ambient air pollution is one of the biggest environmental threats to human health. Being in a region of arid climate, the population is exposed to higher levels of particulate matter and ozone, which increases the risks of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases and lung cancer. Consequently, these health effects will lead to increased economic costs of medical and health infrastructure. Although decreasing in the past years, particulate matter and ozone are still present in ambient air at levels that are not protective of human health. On the other hand, climate change is a global issue that requires urgent attention. The inevitable changes in climatic conditions have crosscutting impacts on all sectors of the city such as the energy sector, health, infrastructure, natural ecosystems, and the economy. In Dubai, the risk to heat-related illnesses, and degradation of coastal habitats and seawater quality associated with climate change are some of the identified foreseen impacts.
In what ways is the initiative innovative?
Dubai considers as the most populated emirate within the United Arab Emirates (UAE). With such increasing population, and new urban developments, sustainable urban planning procedures play an essential role in Dubai’s environmental quality such as air quality, and pollution. Apart from the health risks that air pollution and climate change pose to the citizens, well-being such as life satisfaction and happiness are affected. It disrupts the activities of the affected population as well as their societal functions. The vulnerable population, such as children and the elderlies, and those with underlying conditions, will be more susceptible to the impacts of air pollution. As the impacts of climate change are far-reaching and interrelated affecting all key sectors, the society is faced with great challenges. For example, Dubai is exposed to the risk of flooding which can have huge impact on the infrastructure, natural habitats, and economy. The identified risk to heat-related extreme events also increase mortality, food security and economic productivity.
How is the initiative supported by collaborative working across disciplines and sectors?
The raw data of DMSat1 is acquired by the remote sensing equipment located at the Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre, Dubai. The data is calibrated and processed to produce final images and scientific numerical attributes, which can be easily viewed and further analysed by ArcGIS platform. This final (Level 2) data contains information for each point as an attribute, including longitude, latitude, AOD, AER, concentrations of PM2.5, PM 10 and GHGs.
How does the initiative demonstrate evidence of community support?
The DMSat1 data products are intended to facilitate a broad range of environmental studies and assessments associated with health vulnerabilities due to air pollution and climate change. The DMSat1 data, supported by the in-situ observations acquired by the air quality stations’ network and AI/machine learning techniques, provides an effective way of achieving refined regional environmental inventory and high-resolution modelling.
Implementation, Impact and Replicability
How does the initiative demonstrate evidence of a track record of success against pursued objectives?
Environmental protection has always been at the forefront of Dubai’s and UAE’s development agenda. Accordingly, Dubai’s environmental projects has been always receiving the attention and financial priority among which is the DMSat1. This is in line with the international commitments such as Paris Agreement and C40. It is understood that attainment of this agenda requires concerted efforts across all levels of government and economic sectors. This project support the objectives of the local and national government, which findings and recommendations are aimed at supporting future policy and decision making in the environmental field.
How has the initiative had a ripple effect beyond the scope of the initiative itself, thereby demonstrating a change in the city’s and/or its partners’ way of working with plants?
DMSat1 project is of national strategic significance, supporting a number of emirates and UAE objectives. It is a 1st environmental satellite launched in the Middle East region. Consequently, the project’s objectives, and subsequent resulting studies and decision making has received a significant support from local and national government, academia and private sector.
How have other cities expressed interest in the initiative, or what potential does it have to interest other cities and be customised to their own circumstances?
During the commissioning phase and immediately following the launch, data evaluation and accuracy assessment was performed. It included verification of the instruments performance, raw data quality, fine-tuning the geometric calibration of the data products. In this phase, calibration and validation data imaging were used, which included comparing data with other satellites, existing or other accessible ground-based assets and pre-launch calibration tests. Accuracy assessment of scientific numeric data was also performed at this stage, utilizing ground instruments and accuracy assessments methods.
Sustainability and Resilience
What efforts have been made to reduce the carbon footprint of the initiative?
Beyond the capability of DMSat1 to measure air pollutants and greenhouse gases, the satellite can also support the study of land surface properties and vegetation cover, track the changes in land-use over the UAE region due to urbanization and their impacts on the atmospheric environment, support research on the influences of meteorological conditions and land use to pollutant dispersion, collect evidences on distinct discrepancies in atmospheric pollutant dispersion caused by urban expansion, and provide information on crop management or detecting deforestation.
How have the anticipated impacts of climate change been considered?
DMSat1 contributes effectively to strengthening the leadership role of the UAE in implementing the provisions of the Paris Climate Agreement through the provision of information and data for monitoring greenhouse gas emissions, harnessing advanced technologies and developing advanced mechanisms in monitoring operation, building national capacities to study global warming and supporting developing countries to implement the objectives of the agreement by sharing the environmental data. Additionally, sharing and exchanging of environmental data to international organizations, such as the C40 organization and other countries provides valuable inputs to promote more environmentally sustainable development with significant contribution to the United Nations – Sustainable Development Goals (UN-SDG) priorities.
What processes does the initiative include for it to be considerate in its use of soils and other natural resources?
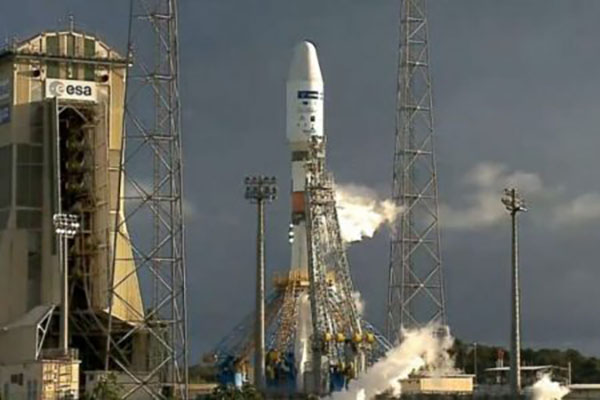
DMSat1 was launched together with other nanosatellites on the same mission, carried by the Soyuz 2.1a rocket. This simultaneous launching reduces the carbon footprint in comparison to launching the satellite separately, which incurs more fuel for the rocket launch. Due to the small size of the satellite, its carbon footprint during its development is smaller compared to traditional satellites. Moreover, the use of advance technology and developing it in an institution that has been efficiently manufacturing satellites both contribute to reduction of carbon footprint. More information on this regard can be find on the following article (https://www.thenationalnews.com/uae/science/we-have-lift-off-uae-s-dmsat-1-satellite-launches-into-space-1.1188844).
Monitoring, Maintenance, and Management
How has the initiative been designed and implemented so that long-term needs for management and maintenance are reduced and can be met?
One of the main objectives of DMSat1 is to measure the levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Monitoring GHGs will provide data which will enable and support actions that Dubai has to prioritize in curbing GHG emissions. Some of these mitigating actions will have co-benefits in terms of adapting to the expected impacts of climate change.
What protocols are in place to facilitate monitoring of results?
DMSat1 is a nanosatellite that is less costly and convenient compared to traditional satellites while delivering the intended objectives. These satellites have relatively short lifespan hence long-term maintenance will not be a burden to Dubai. Additionally, it is built with modern and advanced technology benefitting from the competitive costs of the electronics and other associated industries.
How has the initiative been enhanced in response to monitoring of results?
DMSat1 has a large pre-deployed solar panel capable of generating power greater than 36W, which is complemented by keep-alive solar arrays on all faces to enable power generation in any altitude using renewable energy.