Addressing the urban challenge
Breadth of the issue – How are the problem(s) that are being tackled by your initiative affecting citizens/local businesses or a significant component of the local wildlife?
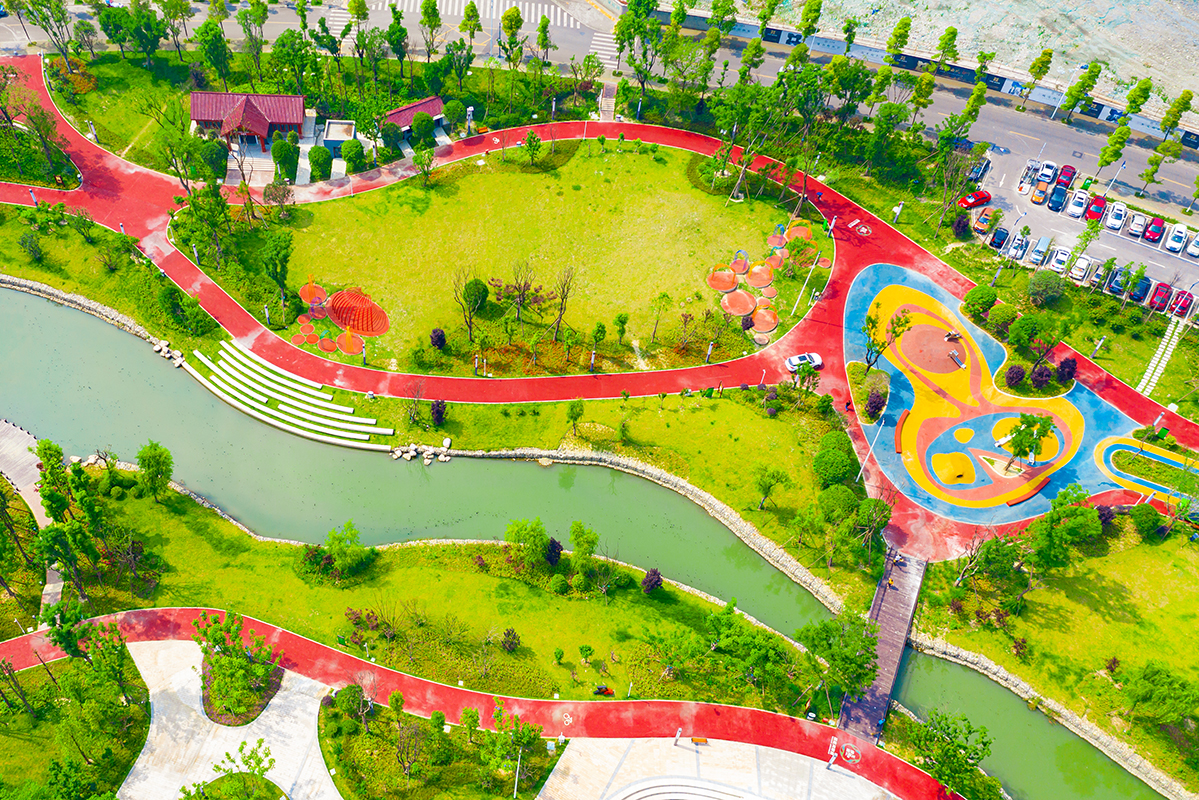
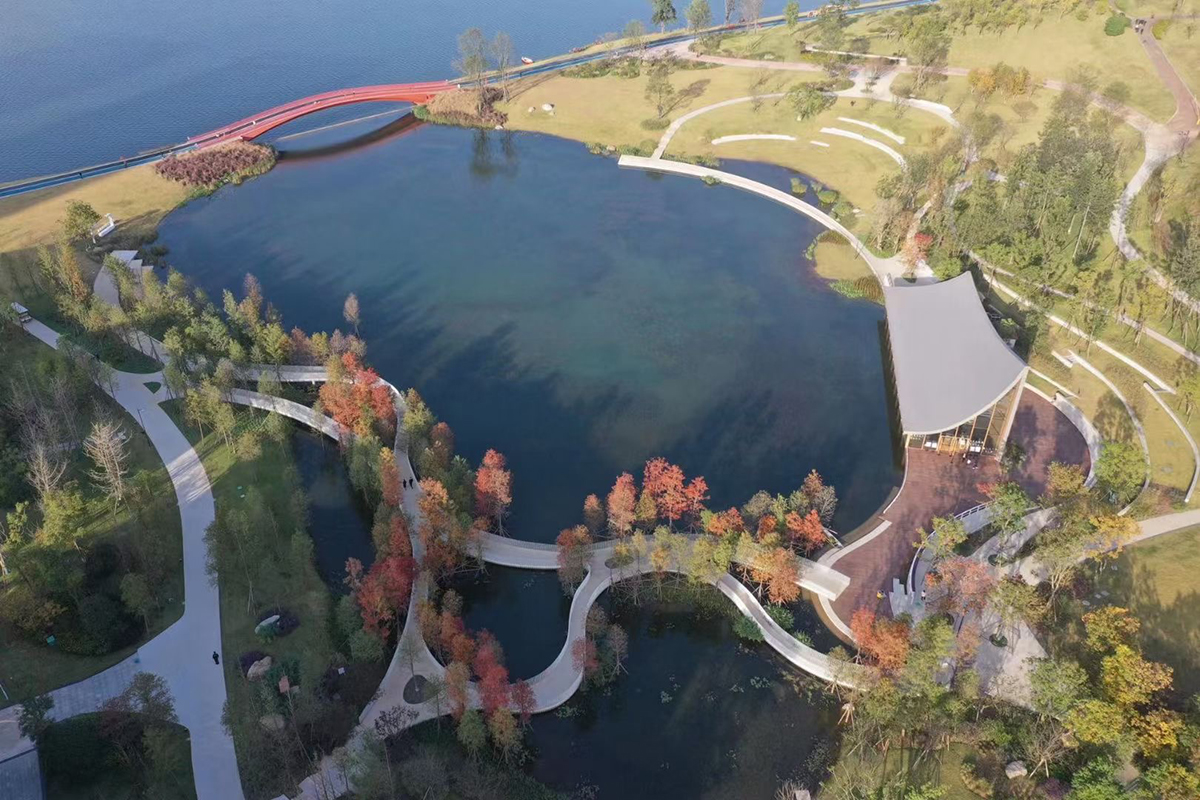
“In some native languages the term for plants translates to ‘those who take care of us’” said Robin Wall Kimmerer, plant ecologist. Scientific evidence behind the greenway concept is plenty, and the ‘patch-corridor-matrix’ principle of landscape ecology represents one of them. Greenways are corridors of land, connecting water systems, mountains, and fields, Linpan natural reserves (a rural settlement type widely distributed in the Chengdu Plain), scenic spots, urban green areas, towns and villages, historical and cultural monuments, and modern industrial parks. Studies show that being outside in a natural and green environment can improve people’s mood and reduce the likelihood of stress-related depression, and more likely to try and help others. Greenway Home initiative increases residents’ green exposure and makes them compassionate about the environment and the community where they live. By incorporating the functions of ecological protection, sports, cultural activities, tourism and emergency shelter, the green corridors now support both the urban and rural residents for their daily activities like walking, cycling, recreation, communication, and education.
Depth of the issue – How seriously are the problems being tackled by your initiative impacting the life of the citizens/businesses/wildlife concerned?
The first benefit is a more balanced ecological system. Community greenways would increase the energy and material flows in the urban ecosystems and make their structures more intricate, and their functions bettered. They would help establish a higher level of equilibrium, in which the systems would regulate itself through negative feedback and better overcome or eliminate external disturbances.
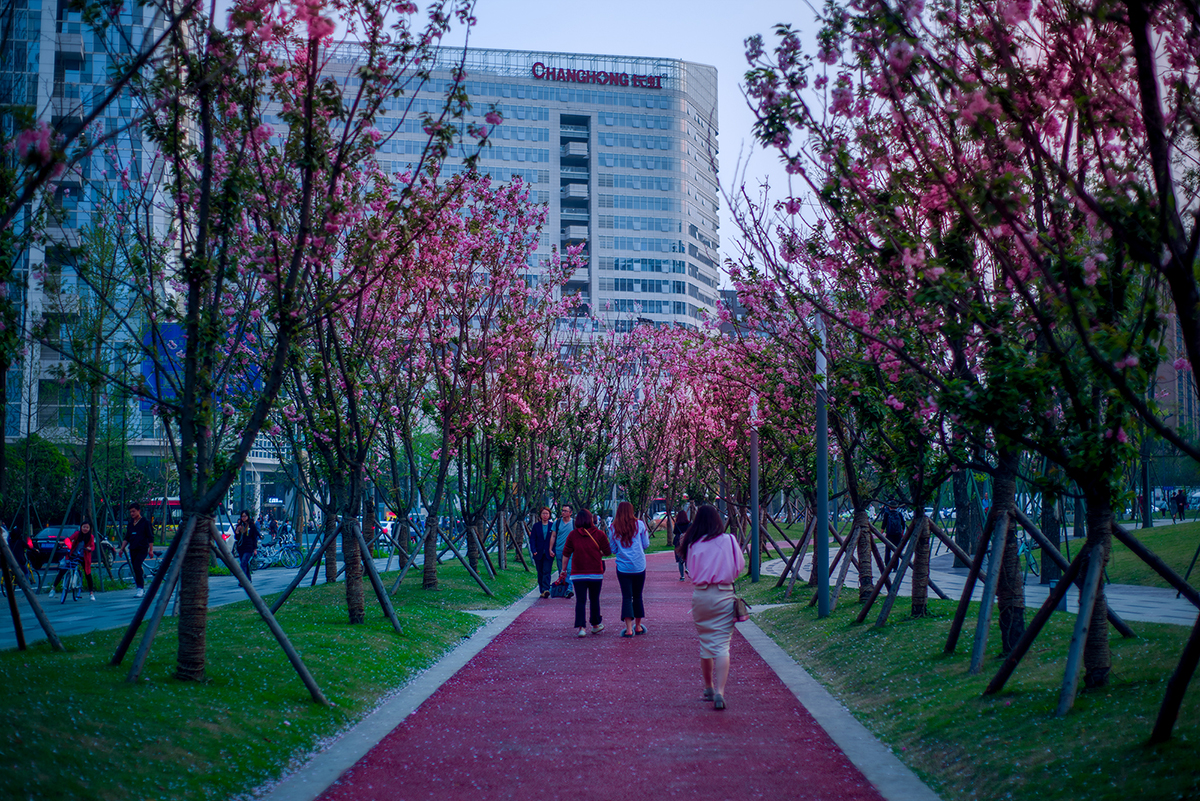
The second benefit is improved liveability and a better life for the residents. Spending time in nature increases people’s vitality, and walking on the greenway generates happiness. By connecting the pocket parks, small recreational gardens, and green spaces, and linking facilities like the kindergartens, health service centres, cultural activity centres, sport and elder care facilities, the community greenways bond the people and nature, and offer the residents easier access to the nature and recreational resources.
The power of plants and natural ecosystems to deliver benefits
How is the initiative shaped by scientific evidence of the potential for plants and natural ecosystems to deliver benefits?
The innovation of this initiative lies in the following: 1)it is a people-centred approach of the Park City initiative. The idea of ‘Greenway Home’ focus on people and address the ‘last mile home’ problem of the community residents. By building the greenways, communities are closely linked with the green spaces, parks, wetlands, and industrial parks. At the same time, different scenes of daily activities and businesses are seamlessly connected, offering people greater accessibility to nature and a better life. 2)the approach focuses on the major challenges of the metropolis, such as the deteriorated ecosystem, traffic congestion, and the busy and fast-paced life. By encouraging people to use the low-carbon and non-motorised transport, which is made possible by the greenways, and by creating laid back vibes along the ways, the approach offers new and greener solutions for people’s commuting, the traffic system, and the ecological environment of the city.
How has the city exploited the potential of plants and associated ecosystems to deliver more than one benefit?
This initiative engaged stakeholders from government departments, design institutions, community residents, and green city advocates. The Chengdu Park City Construction and Management Bureau, in collaboration with the Urban and Rural Community Development and Governance Committee of the CPC Chengdu Municipal Committee and the Chengdu Architectural Design and Research Institute, formulated the guidelines for the ‘Greenway Home’ initiative. Meanwhile, we established a mechanism to seek suggestions from the general public. Community residents are encouraged to offer suggestions for their greenways home’s design, construction, assessment, and maintenance. Moreover, we invited residents, government agencies, and urban designers to join the effort, shaping a greener environment and activating local businesses. ‘Greenway Home’ has indeed become an initiative constructed, governed, and shared by all.
Innovative and Collaborative Solution
How does the initiative show evidence of feasibility, including on-going financial and logistical support?
- Residents’ walking and cycling trails used to be narrow and inconvenient, with no parking space for sharing bikes and illegal parking frequently seen, and they were also in the want of greener when they commute. The Greenway Home initiative addressed those problems by expanding the roads and streets, adopting sponge city programme, and planting more trees along walking and biking trails. So, the residents can commute safely and enjoyable, and in turn they became more willing to choose low-carbon transport.
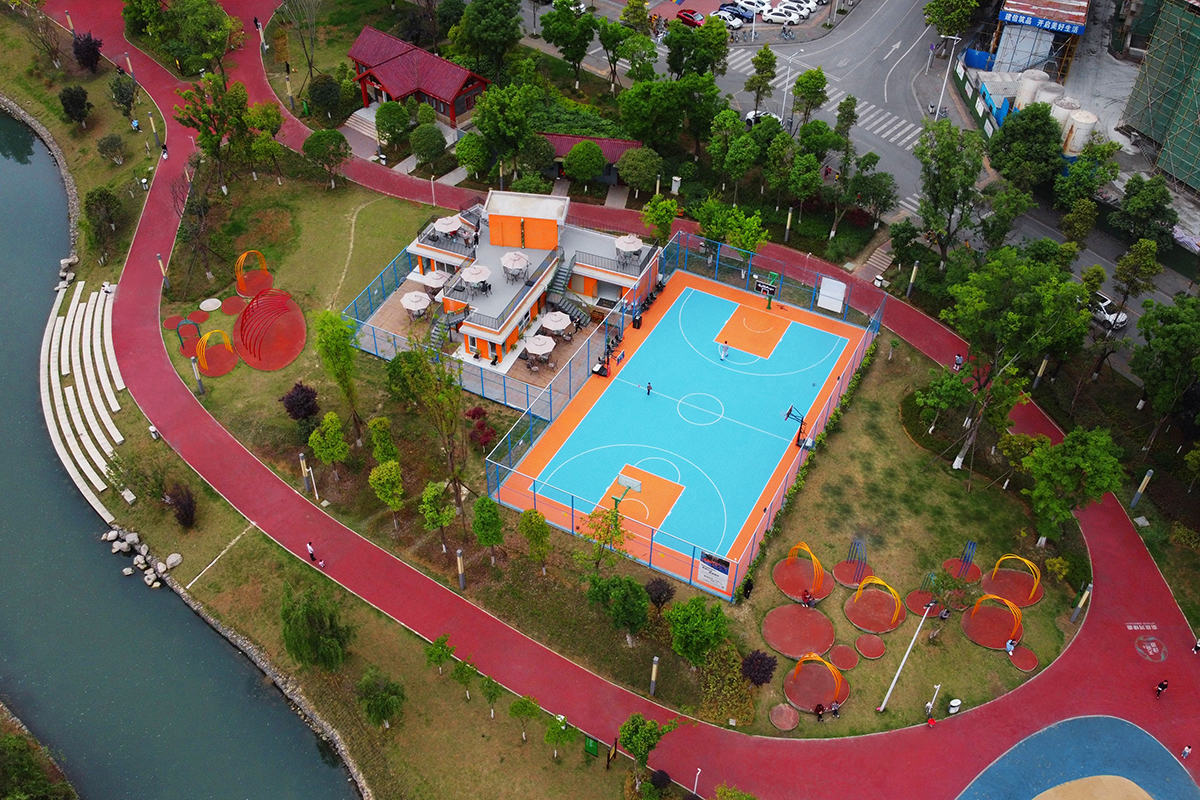
- Residents needed shops, cultural facilities, and eco-friendly social hubs near their homes. Under the Greenway Home initiative, we introduced bookstores, flower shops, grocery stores, and cafes on their way home, so they could enjoy a more convenient community life. The public green spaces, parks, and botanical gardens now become the resident’s social hubs and ideal locations to host educational programmes and special events.
In what ways is the initiative innovative?
The community residents now enjoy:
- more user-friendly trails for walking and biking and safer travel environment; Community residents can now walk or bike downtown the non-motorised transport trails for work, or simply for recreation.
- more convenient and enjoyable commute. Based on the feedback from the residents, we formulated governmental guidance on how and where to set up food and retail businesses along the greenways to better serve the needs of the residents and make their commute more convenient and delightful.
- greener and more eco-friendly streets. While we always chose the more economical and environment-friendly construction modes, the streets in the greenway network become greener and more harmonious with the environment.
How is the initiative supported by collaborative working across disciplines and sectors?
We ensured the alignment between the initiative and the Guidelines for the Integrated Design of the Park City Streets previously issued by Chengdu Municipal Bureau of Urban Planning and Natural Resources, formulated the Guidelines for the Greenway Construction of the Greenway Home Initiative (trial version), and jointly issued the Implementation Plan on Further Enhancing the Greenway Construction of the Greenway Home Initiative with the Urban and Rural Community Development and Governance Committee of the CPC Chengdu Municipal Committee.
How does the initiative demonstrate evidence of community support?
To date, we have altogether built 2,054 sections of community greenways under the brand of ‘Greenway Home’, laid out more than 4,100 facilities, including bookstores, flower shops, cafes, and tea houses. We successfully held the event that has selected the most beautiful ‘Greenway Home’ in across the city. We continued to improve the walking and cycling trails, greenways, and the design of the street crossings. As a result, a slow-paced transport system that is safe, convenient, and comfortable has taken shape.
Implementation, Impact and Replicability
How does the initiative demonstrate evidence of a track record of success against pursued objectives?
The effective quality control and high standard construction come from our multi-pronged mechanism: the annual appraisal system, the timely exchanges and information disclosure, the most beautiful ‘Greenway Home’ ranking, and the best practice replication. Besides, we have given full play to the general public, market entities and the community residents in particular for funding, and has broadened government agencies’ investment channel, which is the dominant source of funding for the initiative.
How has the initiative had a ripple effect beyond the scope of the initiative itself, thereby demonstrating a change in the city’s and/or its partners’ way of working with plants?
By adopting the problem-oriented and demand-oriented approach, we fully solicited residents’ suggestions and conducted surveys on public satisfaction. We chose first to shoot the most prominent problems and meet the most common needs, then to accommodate more diversified needs of the residents by devising detailed plans and attractive events. Feedback showed that we have gained wide recognition from the communities.
How have other cities expressed interest in the initiative, or what potential does it have to interest other cities and be customised to their own circumstances?
Government departments including the Chengdu Park City Construction and Management Bureau, the Urban and Rural Community Development and Governance Committee of the CPC Chengdu Municipal Committeeman the Chengdu Municipal Commission of Urban Management will all be assessed for their performances in the Greenway Home initiative. Coordination meetings and field meetings are two of the working mechanism examples to ensure practical results. Timely exchanges and information disclosure are in place to better advance the projects. We also encourage various kind of model case appraisal to replicate excellent practices and form a ripple effect.
Sustainability and Resilience
What efforts have been made to reduce the carbon footprint of the initiative?
The implementation of the initiative interacted with and involved many other urban renewal initiatives, including the upgrading of small and medium-sized streets, the construction of the city’s industrial functional areas and international communities, the formation of walking and cycling trail network within the parks, the creation of model neighbourhoods, the improvement of community services, and the micro-renewal campaign and safe community campaign of the local communities. The initiative has become a perfect manifestation of the holistic approach for urban management.
How have the anticipated impacts of climate change been considered?
The initiative triggered the following ripple effects: 1) inspired by the greenways, the Park City initiative adopted more new approaches. By connecting community services and facilities for education, health care, cultural activities and elder care, the greenways become interpretations for quality living. 2)long-term vision and international standards became the new benchmark for urban renewal initiatives. The guidelines of the Greenway Home planning are prepared to a high standard and have five highlights— the effect on environmental protection, the display of regional characteristics, the needs for everyday life, tourism, and collaboration among stakeholders. 3) for urban renewal initiatives, culture has gained greater emphasis. Building on the natural, cultural, and industrial resources of the city, and the essence of the 2300-year city history, the facilities and decorations along the Greenway home depict the local narrative of the urban cape, taking viewers on a journey of a historical past, creative present and sustainable future. The Greenway Home initiative has created a greener and more culture-loaded environment for the citizens of Chengdu.
What processes does the initiative include for it to be considerate in its use of soils and other natural resources?
On one hand, by establishing the non-motorised transport system in which more walking and cycling trails are provided, the initiative encouraged greater use of bicycles instead of public transport. As a result, the number of motor vehicles on the road are reduced, so are the carbon emissions. On the other hand, the potential of the native plants is fully tapped, as they have been given full play in the endeavours to create greener environment and greater vegetation coverage. We also spared no efforts to ensure better quality for soil, air, and water, and reduce carbon emissions.
Monitoring, Maintenance, and Management
How has the initiative been designed and implemented so that long-term needs for management and maintenance are reduced and can be met?
Our considerations are:
- while ensuring the diversity and aesthetics of the plants arrangement so that they can be well-presented in all seasons, we chose greener and more economical approaches in building the landscapes.
- we use green and clean energy to light streets, including solar and wind power.
- we adopted the sponge city concept: using low-impact materials to ensure permeable paving, building sunken greenbelt, grassed swales, rain gardens, and smart water retention facilities. The sponge streets helped us reduce water waste and encourage water recycling.
What protocols are in place to facilitate monitoring of results?
The following measures were taken for the projects’ long-term management and maintenance:
- choosing eco-friendly and durable materials. Materials for road paving, facilities and installations were all chosen on eco-friendly, economical, and durable bases.
- formulating the Regulations on the Protection of the Tianfu Greenways, in which we set forth a negative list for the management and maintenance, clarified the responsible entities, and encouraged community residents to participate in the management, maintenance and operation of the projects.
How has the initiative been enhanced in response to monitoring of results?
The Greenway Home initiatives employ both new constructions and renovation of the existing facilities, both are applied mainly to the urban green areas, footpaths, village roads, roads of scenic areas and riverbanks. We forbid motor vehicles to encroach on the greenways and forbid occupying farmlands to build the greenways. We tried the greatest effort to preserve nature and any original landscapes, and reduced waste of land resources by avoiding large-scale excavation and demolition.