Benefits of Urban Greening
Harnessing the Power of Plants
7.5 million trees are planned within the Green Riyadh Programme. All these plants will be irrigated by a network using solely recycled wastewater, which is currently wasted.
Delivering Multiple Benefits
7.5 million new trees will multiply the per capita share of green space. All these plants will be irrigated by a network using only recycled wastewater, which is currently disposed of in desert areas. 99 tree species suitable for ’Riyadh’s environment have been selected for this project.
The project will improve air quality (sequestrate 1,700 tons of PM10, 700,00 tons of GHG etc.). Additionally, it will improve thermal comfort (up to 15 °C of mean radiant temperature under tree canopies).
Consequently, these actions will encourage Riyadh’s citizens to adopt a healthy lifestyle and ultimately transform Riyadh into one of the world’s leading cities, following the strategic goals of the ’Kingdom’s Vision 2030.
The City’s Bold and Innovative Vision
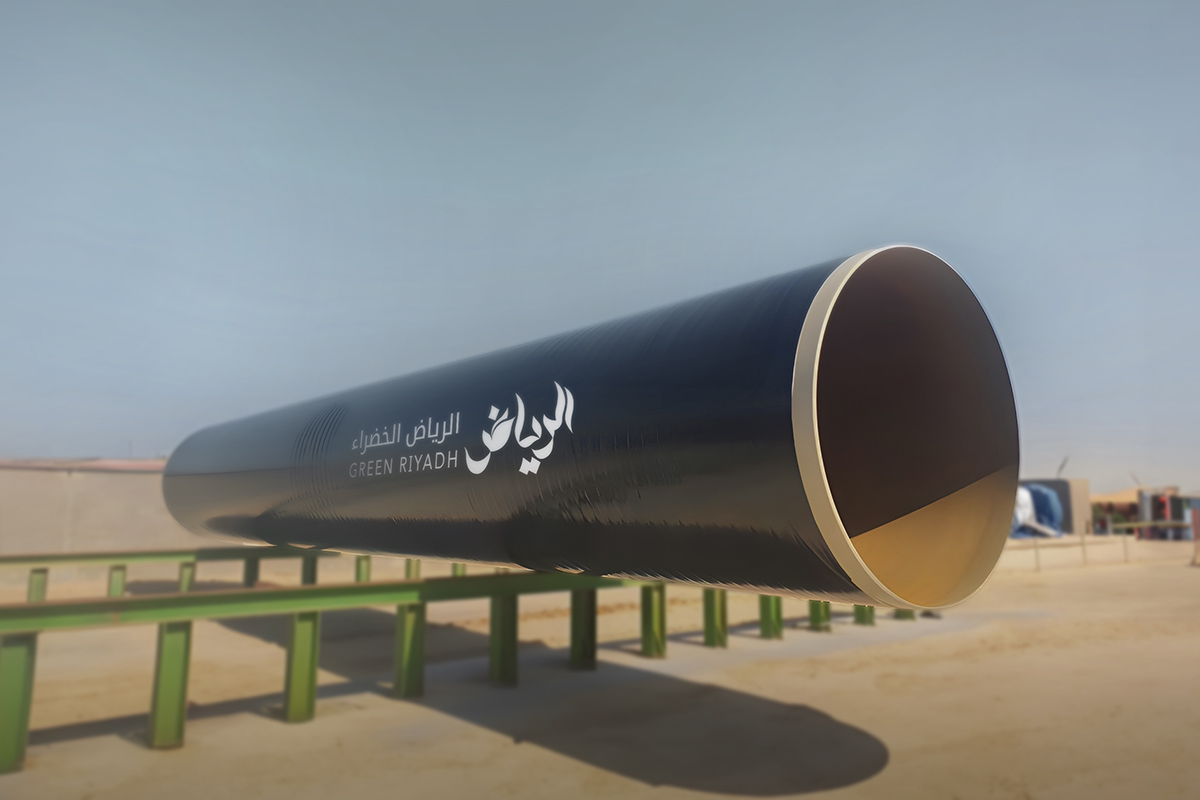
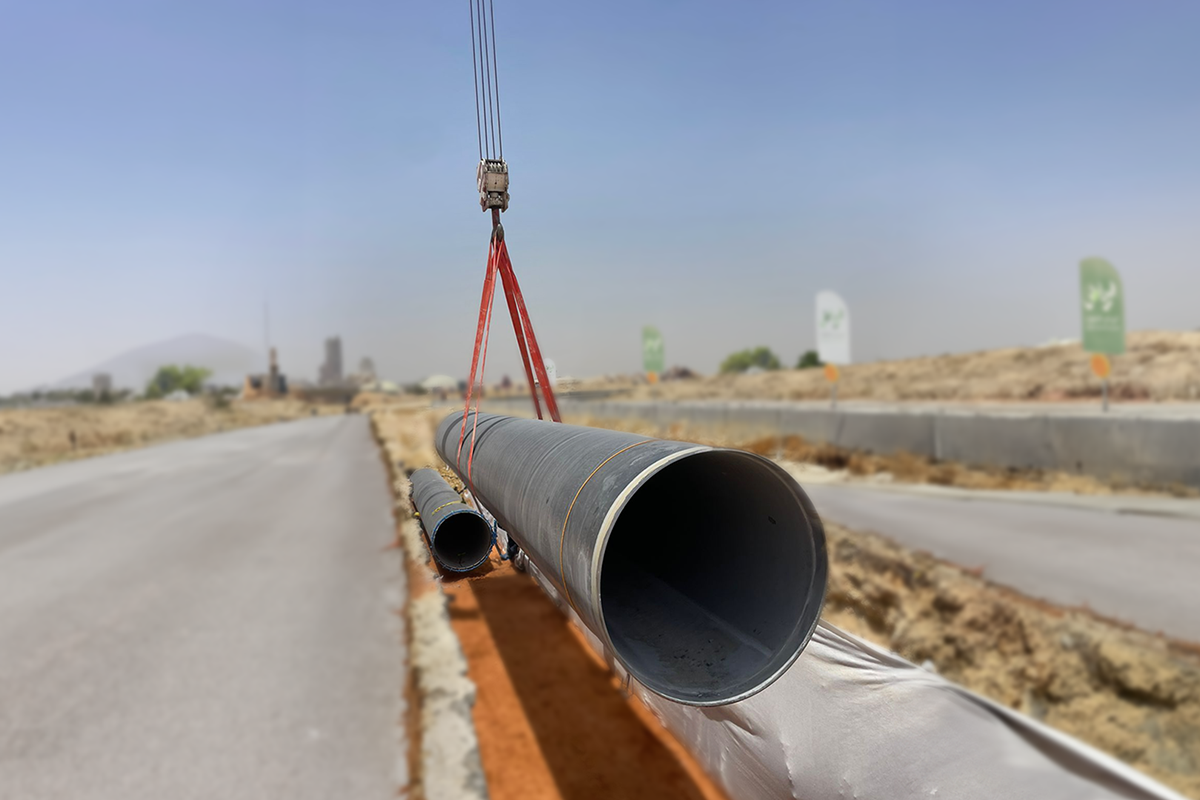
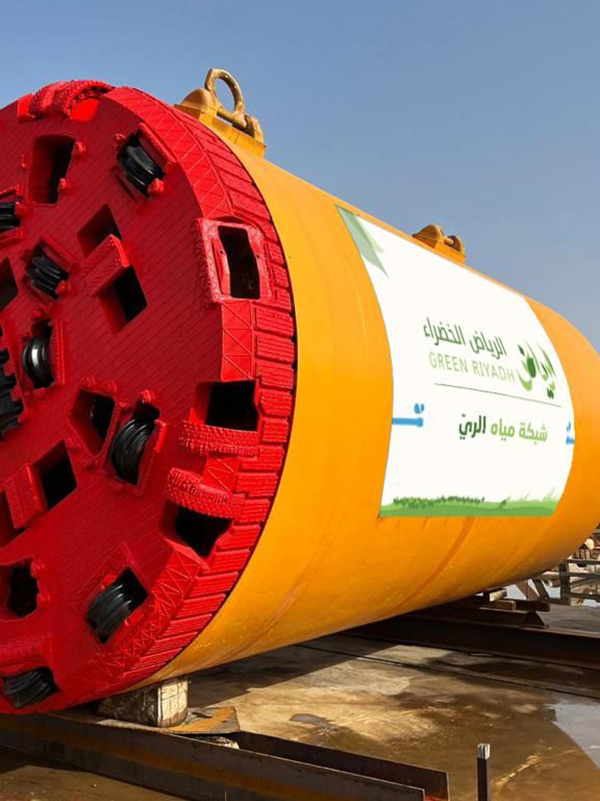
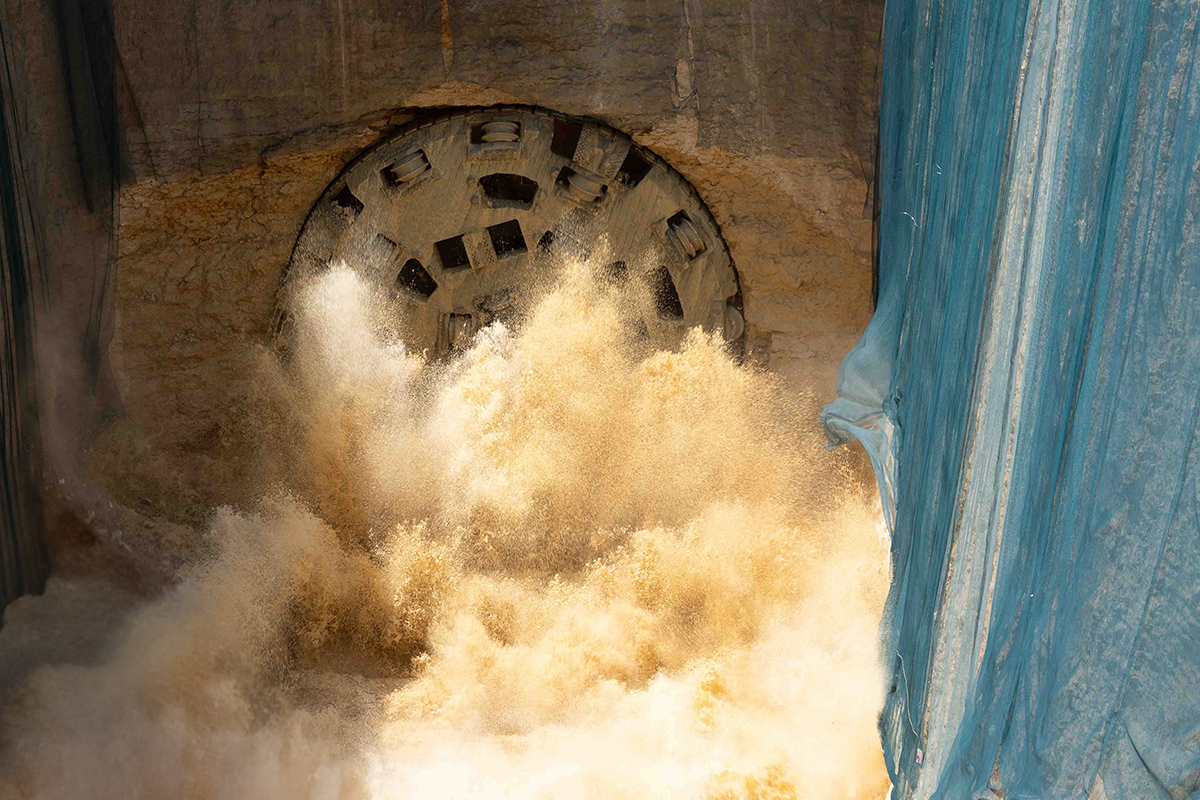
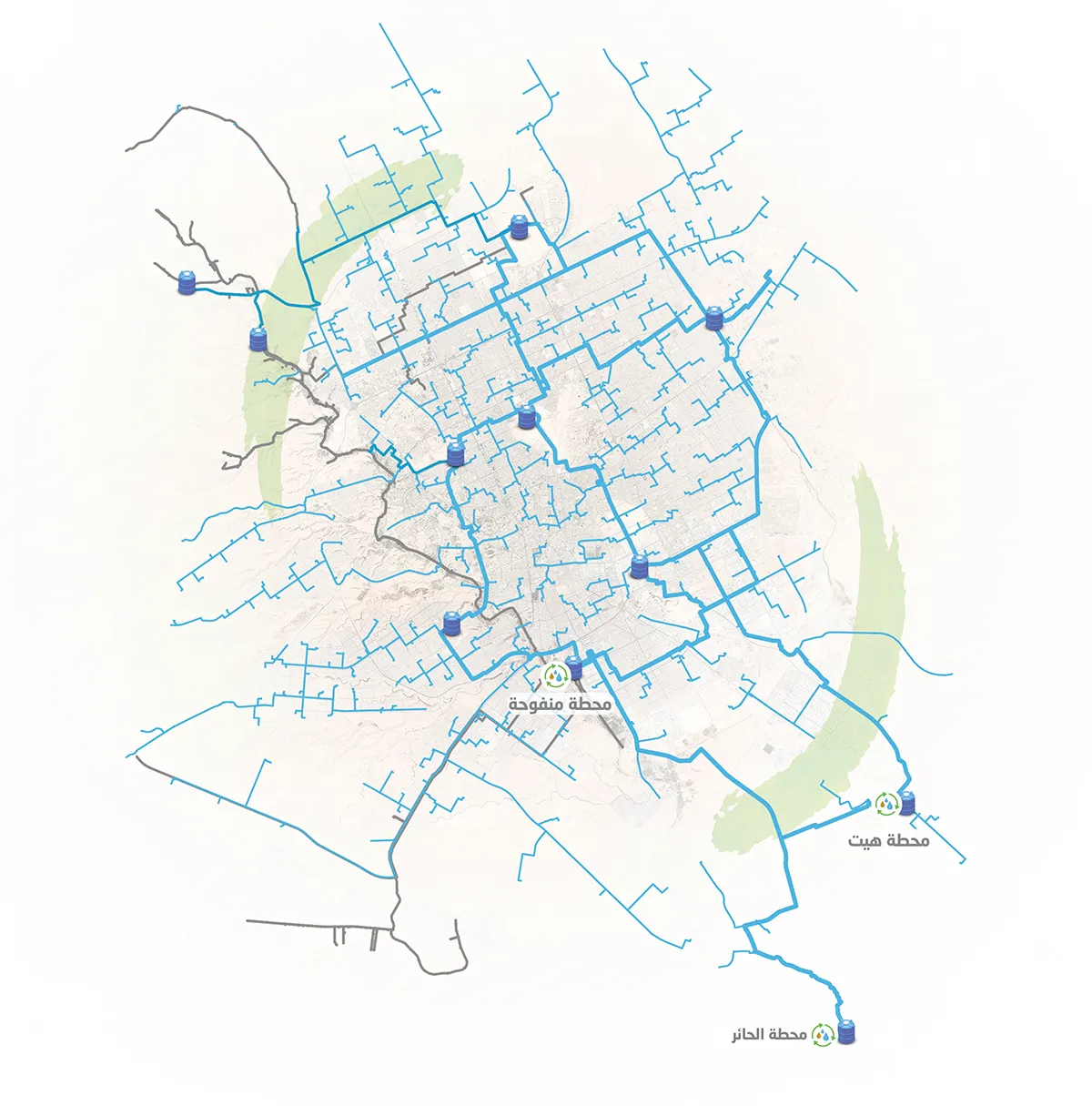
The new treated Irrigation Network will expand all across the metropolitan area with a total length of 1350 kilometres. It will convey 2.7 million cubic metres of treated water daily from the treatment stations to the vegetation areas covering 100% of the irrigation needs.
The diameter of the pipes used in the network range from 1.2 -2.4 metres. A horizontal drilling machine is to be used underneath the main streets so that work can continue without affecting city life.
Partnerships and Collaboration
The Treated Water Irrigation Network is going to cover the whole metropolitan area. The pipelines are being installed under the road network. Building such a network and planning for efficient and sustainable use requires mapping of all the water needs of the city with a 20 year horizon. Extensive stakeholder engagement is required for an intervention of this scale.
A committee composed of relevant government agencies and private entities was established to organise the implementation process.
Addressing Urban Challenges
The Issue
Riyadh was once known as the “Garden City”; however, urban sprawl has changed the city’s character. The city has developed significant green infrastructure projects, but the city’s vegetation and canopy cover currently do not exceed 1.51% and 0.41%, respectively. The project aims to increase the green cover in Riyadh from 1.5% to 9.1% between now and 2030. The objectives of the Green Riyadh Programme include the comprehensive urban, economic, social and cultural development of Riyadh, handling the issues related to environmental management and protection, and providing the city with the necessary public services and utilities.
The Impact of the Issue
Water resources are scarce in Riyadh. This has severe implications for citizens, businesses, and nature. The Green Riyadh Programme aims to address this issue by planting 7.5 million trees and implementing various greening, infrastructure, and enabler projects.
These initiatives recognise the serious barrier of water scarcity and aim to create a better future for the city.
A Nature Orientated Future
By improving the local ecosystem, increasing biodiversity, and employing efficient irrigation techniques, the Programme strives to enhance the lives of the citizens, support economic growth, and ensure a sustainable and greener Riyadh.
Nature Positive Solutions
Implementation
The Green Riyadh initiative is being implemented through a comprehensive strategic plan that includes the following key components:
- Planting trees and other vegetation: The Green Riyadh initiative aims to plant more than 10 million trees and shrubs throughout the city by 2030.
This will be achieved through a variety of green projects, including planting in public parks and gardens, along streets and roads, and on school and university campuses. The initiative is also aiming to establish new green spaces in the city, such as forests and wetlands.
- Improving water efficiency: The Green Riyadh initiative is committed to using only recycled water in order to irrigate the city’s new green spaces. The initiative is working to develop and implement new water-saving technologies, such as drip irrigation and recycled water systems.
- Educating the public: The Green Riyadh initiative is also working to educate the public about the importance of environmental sustainability. The initiative is conducting outreach through schools, community groups and social media.
Feasibility
The feasibility of the Green Riyadh initiative is supported by a number of factors:
- Financial resources: The Saudi government has committed significant financial resources to the Green Riyadh initiative. In 2019, the government announced a US$23 billion investment over the next 10 years. The expected cumulative economic benefit is $2 USD for every USD invested. These account for improved health, real estate etc. The evidence suggests that the Green Riyadh initiative is feasible and that it has the potential to transform the city into a more sustainable and liveable place.
- Technical expertise: The Saudi government has the technical expertise necessary to implement the initiative. Leading international experts are on board to support implementation.
- Public support: The initiative has strong public support. A 2022 survey showed 90% resident support.
The Green Riyadh initiative is still in progress, but it has already made significant advancements in transforming the city into a more sustainable and liveable place. The initiative is expected to have a number of positive benefits for the city, including improved air quality, reduced temperatures and increased access to green space.
Multi-Stakeholder Support
There is strong evidence of stakeholder support for the Green Riyadh initiative. This support comes from a variety of sources, including the government, private sector and civil society.
Saudi government: The Saudi government is the primary stakeholder in the Green Riyadh initiative. It has committed significant financial resources and political support to the initiative. It has also established a number of policies/regulations to support the initiative, such as requiring new developments to include green spaces.
Private sector: The private sector is also a key stakeholder. Private companies are supporting the initiative through financial contributions, in-kind donations and volunteerism.
Civil society: Civil society organisations are also playing a role in supporting the Green Riyadh initiative. Many NGOs are working to educate the public about the importance of environmental sustainability and to promote the initiative. For example, the Green Riyadh Environmental Society is working to plant trees and shrubs in Riyadh and to raise awareness of the importance of environmental protection.
Here are some specific examples of stakeholder support for the Green Riyadh initiative:
- The Saudi government has established a Green Riyadh Fund to finance the initiative. The fund has received contributions from a variety of sources, including the government, the private sector and individuals.
- The Saudi Green Building Council has developed a Green Riyadh Building Code to promote sustainable construction practises in the city. The code has been adopted and is being used to guide the development of new buildings in the city.
Management and Maintenance
The Green Riyadh initiative has been designed and implemented to ensure that long-term needs for management and maintenance are efficient, effective, and can be provided by the city in the following ways:
- Using native and drought-tolerant plants.
- Using water-efficient irrigation systems.
- Establishing a green infrastructure network: The Green Riyadh initiative is establishing a green infrastructure network that will help manage stormwater and reduce flooding.
- Involving the community: The Green Riyadh initiative is working with community groups to plant trees and shrubs and to care for the city’s green spaces. This community involvement will help to ensure that the green spaces are properly maintained in the long term.
Measuring and Reporting Impact
Monitoring Results
The following protocols are in place to facilitate monitoring of results for the Green Riyadh initiative:
Data collection: The Green Riyadh initiative is collecting a wide range of data to monitor results.
This data includes information on the number and type of trees and shrubs planted, the amount of water used to irrigate green spaces, and the quality of the air and water in the city. The data is being collected through a variety of methods, including satellite imagery, ground surveys, and citizen science projects.
Data analysis: The Green Riyadh initiative is using a variety of data analysis techniques to analyse the data that is being collected. This analysis is helping the initiative to track progress on its goals and to identify areas where improvement is needed.
Reporting: The Green Riyadh initiative is regularly reporting on the results of the initiative to the public and to stakeholders. This reporting is helping to keep the public informed about the progress of the initiative and to ensure that the initiative is on track to meet its goals.
The Green Riyadh initiative’s monitoring protocols are essential to the success of the initiative. By tracking progress and identifying areas where improvement is needed, the initiative is able to make adjustments as needed and to ensure that it is on track to meet its goals.
Demonstrating Progress
Monitoring of impact enhances the ability to demonstrate progress in the following ways:
- Tracking progress towards goals: Makes it possible to identify effectiveness and areas of improvement consequently adjusting to ensure that goals are being met.
- Identifying areas of impact: Monitoring helps to identify areas where there is an impact, i.e. improved air quality/reduced temperatures. This is used to demonstrate success and identify opportunities.
- Decision-making: Monitoring provides evidence that can support informed decisions.
- Measurable progress enables Riyadh to expand greening ambitions and attract interest for new projects in the following ways:
- Demonstrating success: Progress demonstrates that the initiative is successful and worth investing in. This can attract interest and funding.
- Building momentum: Progress can help to build momentum. As the initiative achieves its goals, it becomes more likely that it will be successful in the long term.
- Inspiring others: Progress can inspire other cities and countries to implement their own greening initiatives. This can help to create a global movement towards a more sustainable future.
Below are some specific examples of how monitoring impact and measurable progress are enabling Riyadh to expand greening ambitions:
- The initiative has attracted significant attention from the private sector. E.g. Saudi Aramco has committed to planting 10 million trees in Riyadh.
- The initiative has attracted international interest such as the United Nations Environment Programme which partnered to provide technical expertise and financial resources.
- The success of the initiative inspired other cities to implement greening initiatives. E.g., the city of Dubai has launched the Dubai Green Line.
Measuring Impact
The Green Riyadh initiative has achieved a number of significant milestones since its launch in 2019, including:
- Establishing a number of new green spaces, such as the King Salman Park and the Wadi Hanifa Valley.
- Reducing air pollution by an average of 3percent.
- Reducing temperatures in the city by an average of 1 degree Celsius.
- Creating over 100,000 jobs.
The initiative is measuring the impact through a combination of quantitative and qualitative data. Quantitative data includes metrics such as the number of trees and shrubs planted, the amount of water used to irrigate green spaces, and the quality of air and water in the city. Qualitative data includes surveys, interviews and focus groups to collect feedback from residents and stakeholders.
The initiative is reporting on its progress through a variety of channels, including its website, social media and annual reports. The initiative’s website includes a dashboard that tracks key performance indicators such as the number of trees and shrubs planted, the amount of water used to irrigate green spaces, and the quality of the air and water in the city. The initiative’s social media accounts are used to share updates on its progress and to engage with residents and stakeholders. The initiative’s annual reports provide a comprehensive overview of the initiative’s progress and impact.
The initiative’s commitment to measuring and reporting on its impact is essential to its success. By tracking progress and demonstrating success, the initiative is able to attract new resources and inspire others to follow suit.
Learning and Transferability
Adaption and Enhancement
The Green Riyadh initiative is continuously adapting in a number of ways, including:
- Increased focus on sustainability: The project has expanded to include more initiatives aiming to make Riyadh a more sustainable city, such as planting more native trees and shrubs creating green roofs and using recycled materials.
- Coordination with stakeholders: The project team has worked closely with stakeholders, such as residents, businesses and environmental groups, to get their input. This helped ensure the project is meeting the needs of the community and is having a positive impact on the environment.
- Use of technology: The project team is using technology to monitor progress and make adjustments. For example, using drones to survey vegetation and identify areas for additional plantation.
Changes in response to monitoring of progress include:
- Adjusting the planting schedule: Adjusting the planting schedule ensures that trees are planted at the right time to maximise their chances of survival.
- Using more drought-tolerant plants: The project team is using more drought-tolerant plants to reduce the water demand for irrigation.
- Improving public awareness: The project team has launched a number of campaigns to educate residents about the Green Riyadh initiative and how they can contribute to its success.
External stakeholders have played a number of important roles in contributing to the success of the Green Riyadh initiative. For example:
- Residents: Residents have been involved in volunteering to plant trees, providing feedback on progress and reporting environmental problems.
- Businesses: Businesses have been involved by sponsoring tree plantings, donating land,and developing green building initiatives.
Potential for Replication
The Green Riyadh initiative has had a ripple effect beyond the scope of the initiative itself in a number of ways, including:
- Changing the city’s way of working with plants: The Green Riyadh initiative has encouraged the city to take a more holistic approach to urban greening. In the past, the city focused primarily on planting trees in parks and other public spaces. However, the Green Riyadh initiative has shown the importance of integrating green spaces into all aspects of urban planning, from the design of new neighbourhoods to the retrofitting of existing infrastructure.
- Changing partners’ ways of working with plants: The Green Riyadh initiative has also encouraged the city’s partners, such as businesses and residents, to take a more proactive approach to planting and caring for trees. For example, many businesses have started planting trees on their properties and many residents have volunteered to help with tree planting and maintenance.
- Raising awareness of the importance of trees: The Green Riyadh initiative has raised awareness of the importance of trees for both environmental and social reasons. This has led to a greater appreciation of trees among the city’s residents and businesses.
The Green Riyadh initiative has also included transfer of knowledge as part of its design. For example, the project team has worked with international experts to learn about best practises for urban greening. They have also partnered with local universities and research institutions to conduct research on the environmental and social benefits of trees.
Some of the unexpected changes that have occurred due to the progress of the Green Riyadh initiative include:
- Increased demand for trees: The Green Riyadh initiative has led to an increased demand for trees in Riyadh. This has led to a number of new tree nurseries being established in the city.
- Development of new green technologies: The Green Riyadh initiative has also encouraged the development of new green technologies, such as drought-tolerant plants and recycled materials that can be used in construction.
- Greater sense of community pride: The Green Riyadh initiative has also helped to create a greater sense of community pride in Riyadh. Residents are proud to be part of a city that is committed to sustainability and environmental protection.
Overall, the Green Riyadh initiative has had a positive ripple effect beyond the scope of the initiative itself. It has changed the way that the city and its partners work with plants, raised awareness of the importance of trees, and led to the development of new green technologies.
Inspiring Other Cities
Visiting delegations: Delegations from other cities, such as Dubai, Abu Dhabi and Beijing, have visited Riyadh to learn more about the Green Riyadh initiative.
Requests for information: The project team has received a number of requests for information about the Green Riyadh initiative from other cities around the world.
Invitations to speak at conferences: The project team has been invited to speak at conferences about the Green Riyadh initiative, such as the World Urban Forum and the Climate Action Summit.
Other cities can customise the Green Riyadh initiative to their own circumstances in a number of ways. For example, cities in different climates may need to plant different types of trees. Cities with limited land space may need to focus on developing vertical green spaces, such as green roofs and living walls. And cities with limited financial resources may need to focus on low-cost greening initiatives, such as planting street trees and creating community gardens.
The Green Riyadh initiative has the potential to inspire other cities to raise their own urban greening ambitions. The project has shown that it is possible to create a more sustainable and liveable city, even in a challenging environment. Other cities can learn from the successes of the Green Riyadh initiative and implement their own urban greening projects that are tailored to their own circumstances.
Resilience
Reducing Negative Impacts and Ensuring Sustainability
The following efforts have been made to reduce the carbon footprint of the Green Riyadh initiative:
- Planting native trees: The project team is planting native trees, which are more resilient to the local climate and require less water.
- Using recycled materials: The project team is using recycled materials in construction and other aspects of the initiative.
- Promoting sustainable transportation: The project team is promoting sustainable transportation options, such as walking, biking and public transportation.
- Educating the public: The project team is educating the public about the importance of reducing their carbon footprint.
The project team is working with the Riyadh Municipality to develop a new green transportation plan for the city. This plan will promote sustainable transportation options, such as walking, biking and public transportation. This will help to reduce the city’s reliance on cars and reduce its carbon footprint.
The project team is working with local schools and community groups to educate the public about the importance of reducing their carbon footprint. This includes teaching people about the benefits of planting trees, using recycled materials, and choosing sustainable transportation options.
Environmental Considerations
The anticipated impacts of the Green Riyadh initiative on the environment have been considered in a number of ways, including:
Plant selection
- Diversification: The project team is planting a variety of native and non-native trees and shrubs to ensure that the city’s green spaces are diversified and resilient.
- Suitability to present and anticipated local microclimate: The project team is selecting plants that are well-suited to the current and anticipated microclimate of Riyadh. This includes selecting drought-tolerant plants and plants that can withstand high temperatures.
- Procurement: The project team is procuring plants from local nurseries to reduce the carbon footprint of transportation.
Access to water
- Recycled water: The project team is using recycled water to irrigate the city’s green spaces whenever possible.
Energy efficiency and recycling
- Energy-efficient irrigation systems: The project team is using energy-efficient irrigation systems to reduce the amount of energy used to water the city’s green spaces.
- Recycling of green waste: The project team is recycling green waste, such as leaves and branches, to produce compost and other products. This helps to reduce the amount of waste that is sent to landfills.
Use of Natural Resources
The Green Riyadh initiative has considered the use of natural resources to ensure that it is sustainable and resilient in the following ways:
Soils
- The project team is using local soils whenever possible. This reduces the need to transport topsoil from the countryside, which can damage ecosystems and increase the carbon footprint of the project.
- The project team is improving the quality of existing soils by adding organic matter and compost. This helps to improve soil fertility and water retention, which makes the soil more resilient to drought and other stresses.
Water
- The project team is using recycled water to irrigate the city’s green spaces whenever possible. This helps to conserve the city’s water resources and reduce its reliance on desalination, which is a very energy-intensive process.
- The project team is using drip irrigation systems to reduce water consumption. Drip irrigation systems deliver water directly to the roots of plants, which reduces evaporation and runoff.
Other natural resources
- The project team is using native plants whenever possible. Native plants are well-adapted to the local climate and require less water and fertiliser than non-native plants.
- The project team is using organic fertilisers and pesticides whenever possible. This helps to protect the environment and reduce the use of synthetic chemicals.
- The project team is minimising the use of machinery and equipment. This helps to reduce the carbon footprint of the project and conserve natural resources.