Benefits of Urban Greening
Harnessing the Power of Plants
The initiative, based on the New Urban Agenda and the Sustainable Development Goals, understands the importance of the environment to the city, and of its role in enhancing citizen welfare. Its main focus is the potential benefit of the natural ecosystem for Belo Horizonte and its infrastructure. Greening BH seeks to expand the city’s green urban spaces, not only in terms of preservation, but also to amplify the cultural and public appropriation of these places. In order to achieve the environment’s full beneficial potential for Belo Horizonte’s citizens, they must be able to use these spaces as a source of leisure and recreation. Therefore, many of the initiatives envisaged in Greening BH, such as the creation of linear parks, take into account the potential for public use of protected spaces, while also maintaining their original preservation objectives.
Delivering Multiple Benefits
Greening BH is included in the New Master Plan, a document that defines the public policy guidelines to be adopted by the municipal administration. As such, investment in the project, through the allocation of funds, is planned on an annual basis, and implementation takes place through the City Hall and its secretariats. Greening BH envisages using the plants both to preserve and improve the well-being of Belo Horizonte’s citizens. In addition, the project envisages using the plants to provide human food and contribute to the food security of the people, especially families in situations of social and economic vulnerability. This happens through Urban Agroforestry.
The City’s Bold and Innovative Vision
Greening BH combines a series of different parallel actions, mentioned above, which together aim to make the city greener and more pleasant. Among these initiatives, we have the Ladybug Biofactory and Urban Agroforestry as highlights in terms of innovation.
The Ladybug Biofactory serves a purpose of biological pest control. It’s a nature-based solution to the problems caused by the uncontrolled growth of whiteflies, which ladybugs are natural predators of. These pests predominantly infest Ficus macrocarpa trees in areas where these trees line the streets and have been declared as Cultural Heritage by the Municipality. The Biofactory was structured to accommodate the needs for insect management in urban agricultural initiatives, including community gardens and backyards that cultivate food. By controlling and regulating the population of undesired insects, the Biofactory boosts the variety of biological control agents, thereby augmenting the overall effectiveness of pest control.
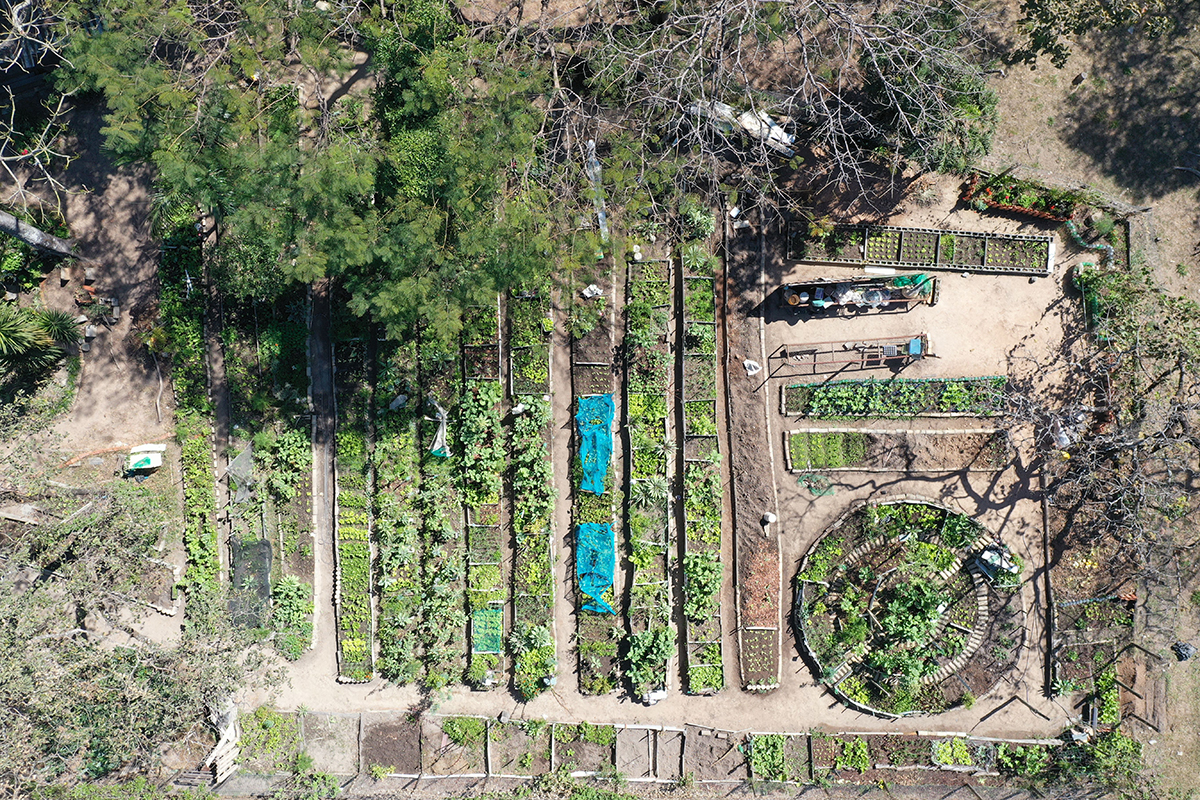
Urban Agroforestry plays a crucial role of providing a space for socially vulnerable families to be able to grow their own food while still living in the city, while also protecting the environment and the local biome and its species.
Partnerships and Collaboration
Greening BH is implemented by the City Hall, through a scope of various secretariats. Mainly, the Municipal Secretariat of Urban Planning, the Municipal Secretariat of Urban Policy are responsible for the project, with participation from the Municipal Secretariat of Environment, the Municipal Parks and Zoo Botany Foundation, the Capital Development Superintendence, the Belo Horizonte Urbanization and Housing Company, the Municipal Secretariat of Works and Infrastructure and the Office of International Relations.
Addressing Urban Challenges
The Issue
Greening BH was designed to mitigate the city’s environmental problems, caused mainly by fires, floods and overall carelessness. Faced with the growing climate crisis experienced by everyone, and the increasing degree of instability of natural phenomena such as precipitation, the maintenance and expansion of urban green areas is necessary to ensure the well-being of the population and the improvement of urban space, as well as the city’s resilience in the face of these problems. Elements of the project, such as Agroforestry, also have economic and social impacts. Agroforestry ensures a source of food for socially vulnerable families, and also a source of income, as these families can market what they produce in the areas they occupy.
The Impact of the Issue
Faced with the problems caused by global warming and natural disasters, plants act in the urban environment as providers of well-being and as agents that increase urban resilience. Linear parks play an important role in preventing floods. Pest control by ladybugs avoids the misuse of pesticides in places with high circulation of people. Increasing the number of green areas in general, through parks, pocket forests, urban agroforestry, flowerbeds, etc., helps to make the city’s temperature more pleasant, especially in the face of heatwaves. Greening BH brings together a wide range of initiatives that are individually concerned with promoting nature-based solutions to the problems presented.
Nature Positive Solutions
Implementation
Greening BH is part of the New Master Plan, which was institutionalized in 2019. Some of the projects that are included in Greening BH are still being designed, or have just begun being implemented. Some of its initiatives, though, have been in course since before the institutionalization of the Master Plan.
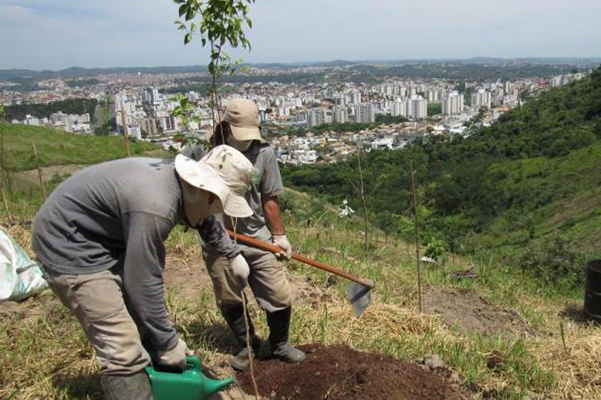
The Montes Verdes project was created in 2017, to induce the recovery and revegetation of degraded areas in Belo Horizonte. Starting in the Serra do Engenho Nogueira area and Parque Fernando Sabino, in Pampulha, the project expanded and recovered other areas of the municipality, including the slopes in communities such as Morro das Pedras, Vila Cemig and Santa Lúcia. Since its implementation, Montes Verdes has already recovered more than 10 thousand hectares of green area and planted around 30 thousand new seedlings.
The implementation of Urban Agroforestry began in 2018. In 2019, the city had 41 Community Collective Production Units, and, as of today, that number has grown into 56 Units. Beside that, there are over 250 Institutional Production Units, that operate within public facilities such as schools, health centers, etc., whereas in 2019 there were around 127 Units.
The Ladybug Biofactory began in 2019, and features a 40 m2 climate-controlled laboratory, outfitted with plastic pots for breeding and acrylic containers for distribution.
Feasibility
Greening BH is feasible for the city because it is included in the New Master Plan. Therefore, its initiatives have their own budget and their own teams for implementation and maintenance.
Multi-Stakeholder Support
As mentioned above, the project is carried out by the City Hall, through a diverse scope of secretariats.
Management and Maintenance
The program’s longevity is guaranteed by its inclusion in Belo Horizonte’s Master Plan. The parameters established by Greening BH in terms of preservation and the city’s total green area must be respected and maintained as new interventions are made in the urban space. The project also provides parameters for private initiatives in the city to also maintain a high level of care for green areas. As such, these initiatives must always include sustainable elements in their projects that compensate for the impact they cause. The challenges encountered in implementing the project do not concern identifying the spaces to be worked on, as this has already been done in the Greening BH mapping. Thus, possible difficulties encountered in the green interventions to be carried out have already been foreseen. The main challenge encountered concerns the degree of demand placed on private initiative in their projects, which could lead to a possible emptying of these interventions. To prevent this from happening, the law must remain flexible in this case.
Measuring and Reporting Impact
Monitoring Results
Belo Horizonte’s sustainable urbanization policy, set out in the New Master Plan, together with the requirements made for private initiatives in the municipality in the urban space, provide for new developments to be evaluated and reviewed by the Municipal Secretariat of Environment. Through this body’s team, the proposals presented can be altered and improved before they are approved and started. The projects that are part of Greening BH were studied and evaluated as viable nature-based solutions for Belo Horizonte to achieve its environmental and climate goals, even before the Master Plan was approved and put into practice. Therefore, the interventions are based on technical and scientific evaluations, and have proven to be necessary for the well-being and resilience of the city.
Demonstrating Progress
The monitoring of the impact of the projects carried out by Greening BH began before the implementation of the New Master Plan, and continues at each stage of the project. Initially, the chosen initiatives had their feasibility and effectiveness studied and analyzed. The entire process of implementing the projects is monitored by the Municipal Secretariat for Urban Policy, which uses its regulatory tools to assess compliance with the interventions. In addition, the Municipal Secretariat of Environment has technical and scientific instruments to monitor the impact of projects on the urban environment. This is done, for example, by cross-referencing information. More specifically, Belo Horizonte carries out annual calculations and monitoring that determine the city’s greenhouse gas emissions, the mapping of its geological risk areas, among others. Through the results obtained in these reports, it is possible to monitor the effectiveness of the green interventions carried out.
Measuring Impact
As mentioned before, many of the actions foreseen by the New Master Plan are still being designed and implemented. Therefore, there are few to no records of how measurement is being done, or how it has affected the further implementation of the actions.
Learning and Transferability
Adaption and Enhancement
As mentioned before, many of the actions foreseen by the New Master Plan are still being designed and implemented. Therefore, there are few records of how measurement has affected the further implementation of the actions.
Potential for Replication
As mentioned earlier, Greening BH provides for interventions carried out by the private sector to include sustainable elements in their planning and construction. In order for this to happen effectively, Belo Horizonte City Hall offers consultancy services through its departments so that companies can understand the best way to comply with the requirements. One of the consequences of this is that this knowledge, acquired by the companies, can be applied to other works carried out, generating a greater positive impact than initially planned.
Inspiring Other Cities
Parts of Greening BH, such as Urban Agroforestry and the Ladybug Factory, have received a share of international attention, and have been recognized as innovative, nature-based solutions for urban problems. Both projects have been published by the platform Use Metropolis, to serve as inspiration for other cities abroad. The Ladybug Factory, especially, has inspired the city of Nice, in France, to implement a similar project. Belo Horizonte has shared its experience with Nice to help with their implementation.
Resilience
Reducing Negative Impacts and Ensuring Sustainability
The Greening BH initiative has been designed and is being implemented with the decrease of the carbon footprint of the whole city in mind.
Environmental Considerations
Belo Horizonte City Hall offers a range of possible green actions for private initiatives to offset the impact of their interventions in the urban space. These solutions have been developed on the basis of a series of technical and scientific studies, taking into account the needs of the municipality and the possibilities of the environment in question. These solutions can be green, meaning that they use plants in their implementation, or blue, meaning that they use water. In the case of green solutions, the local biome, Cerrado, is taken into account, and the plants used are generally native to the region.
Use of Natural Resources
Greening BH was developed in order to utilize and enhance the environmental attributes that already exist in the municipality, taking into account good practices that are already underway and have already proven effective, as well as the region’s natural biome. Many of the existing projects in Greening BH are recognized regionally and internationally, and are based on international parameters, since the New Master Plan was inspired by the SDGs, the New Urban Agenda and the Paris Agreement.