Addressing the urban challenge
Breadth of the issue – How are the problem(s) that are being tackled by your initiative affecting citizens/local businesses or a significant component of the local wildlife?
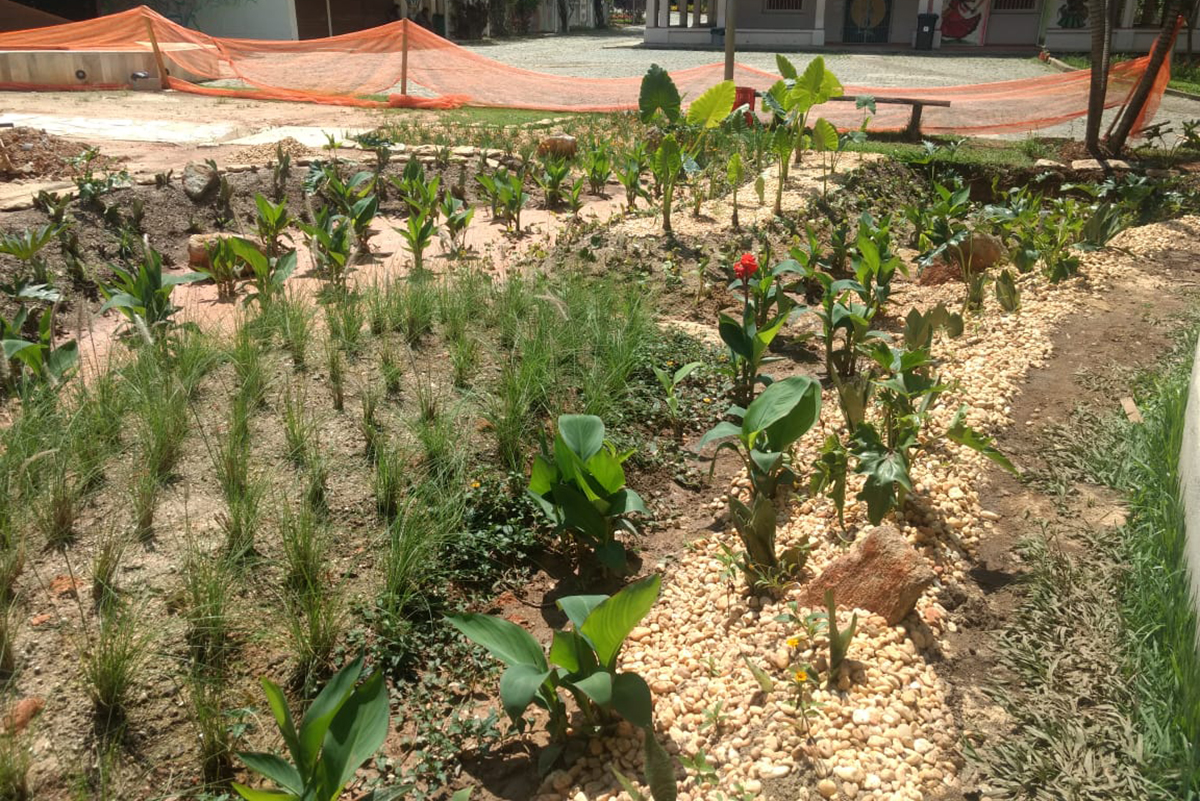
According to ICLEI, the implementation of rain gardens contributes to rainwater runoff, allowing the water to be filtered by the vegetation and to infiltrate the soil. This type of solution helps recharge the water table, increases biodiversity, and improves the local microclimate and air quality. The institution is formed with specialists in the area, who through scientific evidence implement the project aiming at the best sustainable performance for the city.
Depth of the issue – How seriously are the problems being tackled by your initiative impacting the life of the citizens/businesses/wildlife concerned?
When implemented, rain gardens retain part of the rainfall runoff, contribute to reduced flood risk, improve water and soil quality, therefore, in addition to retaining the water from the heavy rains of Belo Horizonte, it also promotes local biodiversity.
The plant species planted attract local wildlife that act as pollinators and ecological pest control. Insects such as ladybugs, scissors, butterflies, lacewings, bees, and solitary wasps need shelter to live near the garden. Sticks, wood scraps, leaves, and other natural elements can be gathered together to create shelter from sun, rain, and wind.
The power of plants and natural ecosystems to deliver benefits
How is the initiative shaped by scientific evidence of the potential for plants and natural ecosystems to deliver benefits?
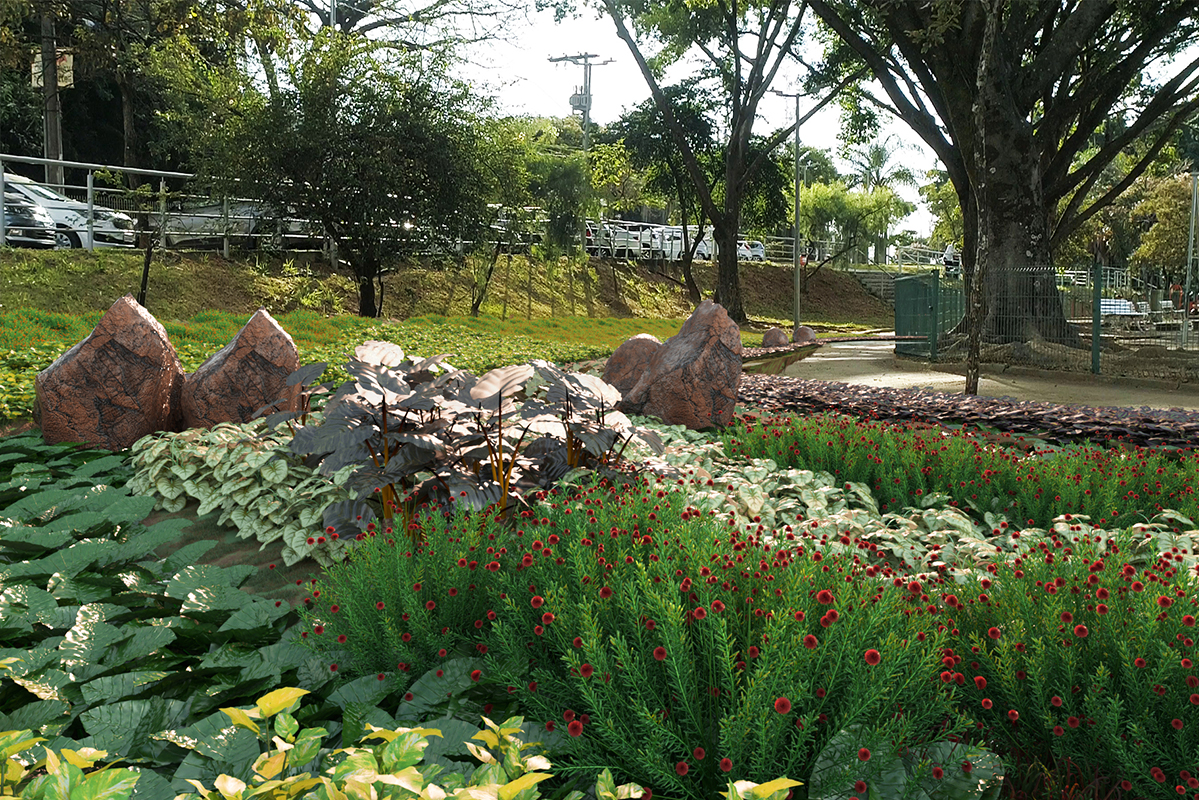
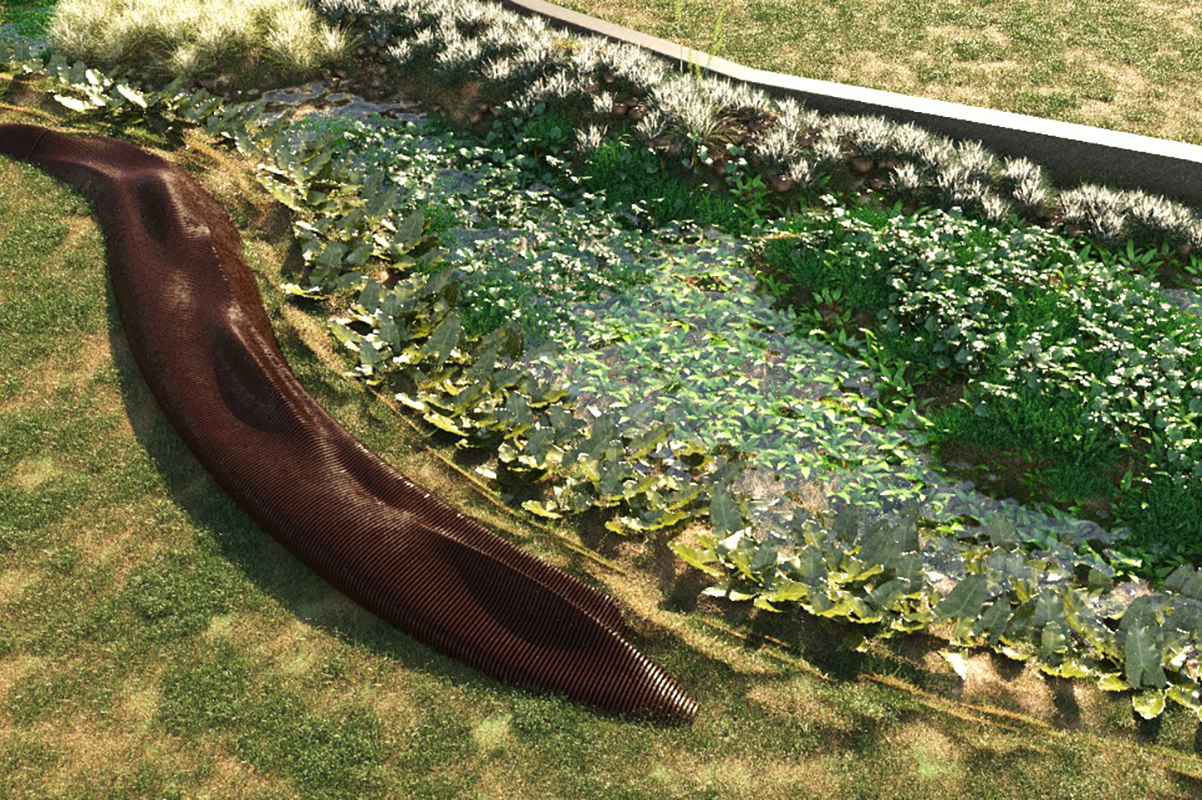
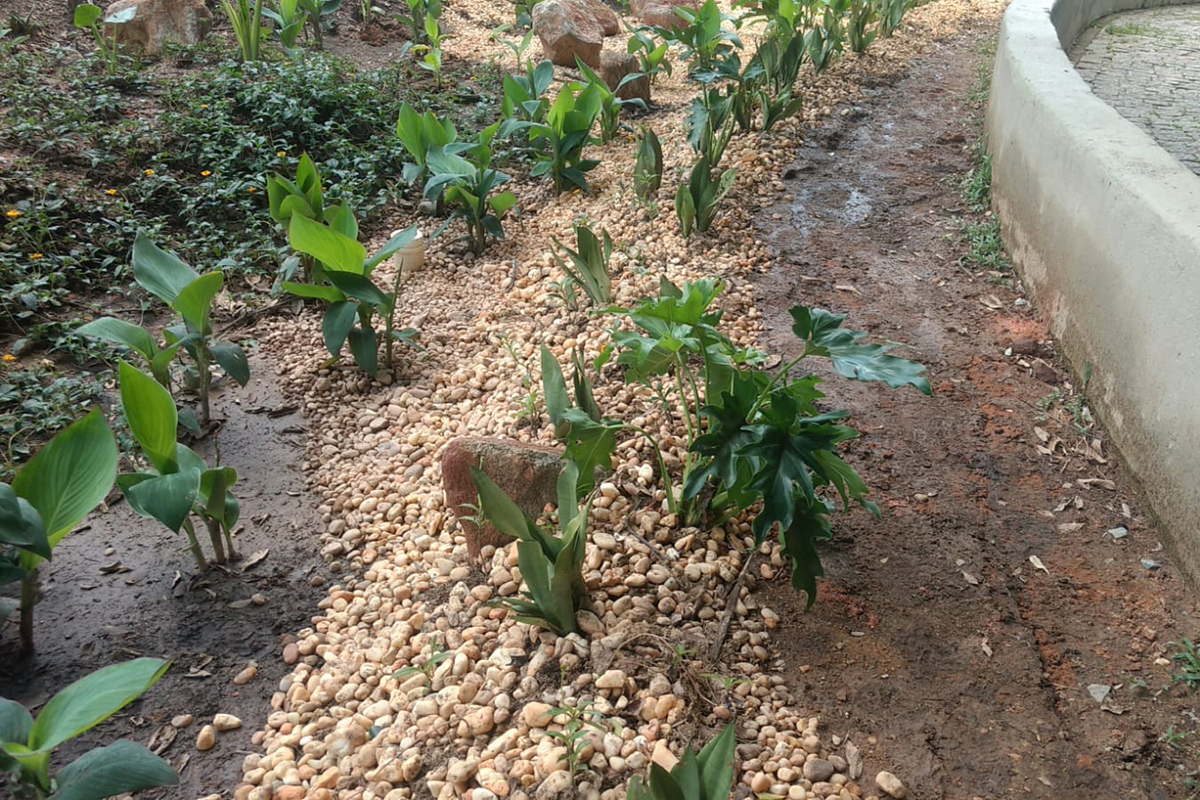
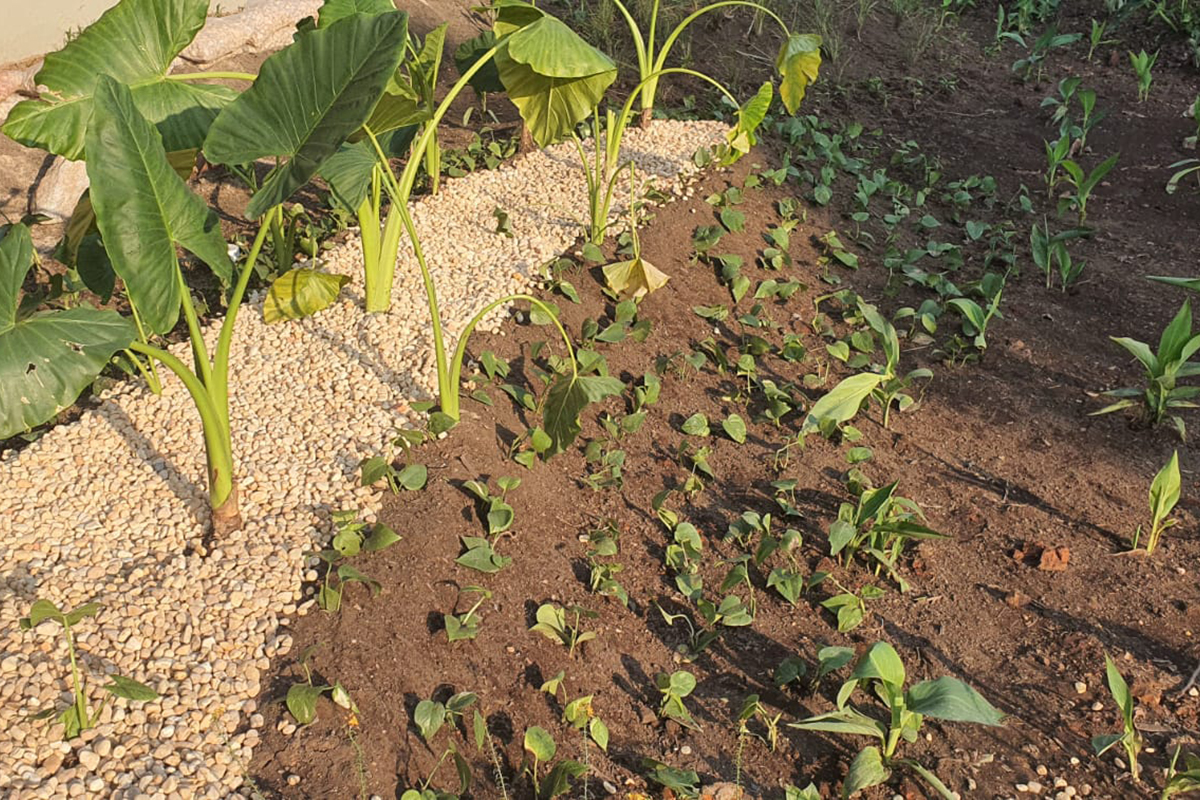
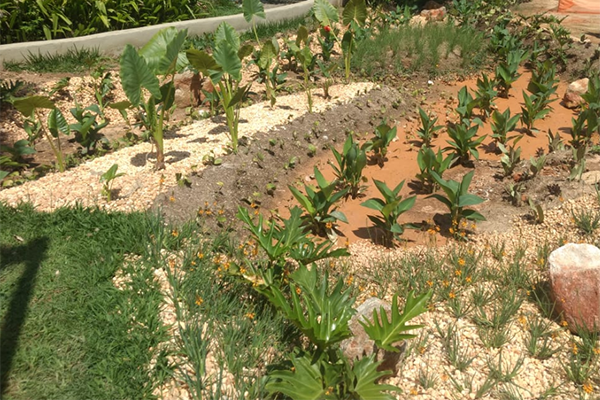
The rain garden is a bioretention system, this measure uses the biological activity of plants and microorganisms to remove pollutants from stormwater, and contributes to the infiltration and retention of precipitated water volumes. In general, these structures can be described as shallow depressions of earth, which receive runoff water. The water flows accumulate in the depressions forming small puddles, and gradually the water is infiltrated into the soil. Pollutants are removed by adsorption, filtration, volatilization, ion exchange, and decomposition. The clean water can be infiltrated into the ground for aquifer recharge or collected in a drain and discharged into the micro drainage system. In the case of rainfall events that exceed the capacity for which the structure was designed, the excess flow is diverted from the area and routed directly into the drainage system.
How has the city exploited the potential of plants and associated ecosystems to deliver more than one benefit?
The project counts on the academic participation of researchers in the area, students and professors from related undergraduate courses: Architecture, Environmental Engineering, Civil Engineering, Biology.
It is important to emphasize that the local community is also involved in counting the participation of its representatives in webinars, for raising awareness of the importance of garden creation.
Innovative and Collaborative Solution
How does the initiative show evidence of feasibility, including on-going financial and logistical support?
The metropolitan region of Belo Horizonte has faced heavy rains in the last years, generating losses to the city’s structure and to the population. In January the metropolitan region received an average volume of more than 160 millimetres of water, according to data from the National Centre for Monitoring and Alerts of Natural Disasters (Cemaden), This is the highest number in the last 30 years. Therefore, the creation of a rain garden aims to reduce the damage caused by this phenomenon of nature. Water retention with the use of the garden´s plants contributes substantially to turn a harmful situation into a sustainable opportunity.
In what ways is the initiative innovative?
The metropolitan region of Belo Horizonte has faced heavy rains in the last years, generating losses to the city’s structure and to the population. In January, the metropolitan region received an average volume of more than 160 millimetres of water, according to data from the National Centre for Monitoring and Alerts of Natural Disasters (Cemaden), This is the highest number in the last 30 years. Therefore, the creation of a rain garden aims to reduce the damage caused by this phenomenon of nature. Water retention with the use of the garden´s plants contributes substantially to turn a harmful situation into a sustainable opportunity.
The INTERACT-Bio project was financed by the German government through ICLEI, Local Governments for Sustainability, a global network for sustainable development. The initiative of the city of Belo Horizonte in seeking for funding and carrying out a model of sustainable development on an international basis demonstrates the city’s incentive to promote good practices and become an international success example.
It is also worth mentioning that the company responsible for the architectural execution of the project (Guajava) was positively impacted, pointing in its official media as an example of success. Representatives of the environmental council, the Regional Council of Engineering and Agronomy, and the federation of industries of the state of Minas Gerais attended meetings about INTERACT-Bio to arouse the interest of investors in nature-based solutions.
How is the initiative supported by collaborative working across disciplines and sectors?
The monitoring protocols are separated in four sections: Watering of Shrubs and groundcover; Shrub pruning; Plant Health evaluation; Waterline analysis; cleaning of water spillways.
How does the initiative demonstrate evidence of community support?
According to the Secretary of the Environment, evidence shows that there was an environmental compensation of 64,969.94 Euros from the municipality.
Implementation, Impact and Replicability
How does the initiative demonstrate evidence of a track record of success against pursued objectives?
To obtain the funding, it was agreed that the municipality must submit an updated work plan for the execution of the contract products within the specifications mentioned in the terms of reference. The documents, which require the commitment of the participants, along with the secrecy of legal issues involving the security of both parties. The project has financial transparency and the city hall publicly revealed that it received 50,000 Euros within the partnership with the German government.
How has the initiative had a ripple effect beyond the scope of the initiative itself, thereby demonstrating a change in the city’s and/or its partners’ way of working with plants?
For the local community, the team responsible for the propagation of the project has created playful signs to inform about the importance of the park. It also included the realization of a webinar, available at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d-8tzIa0Ld0
How have other cities expressed interest in the initiative, or what potential does it have to interest other cities and be customised to their own circumstances?
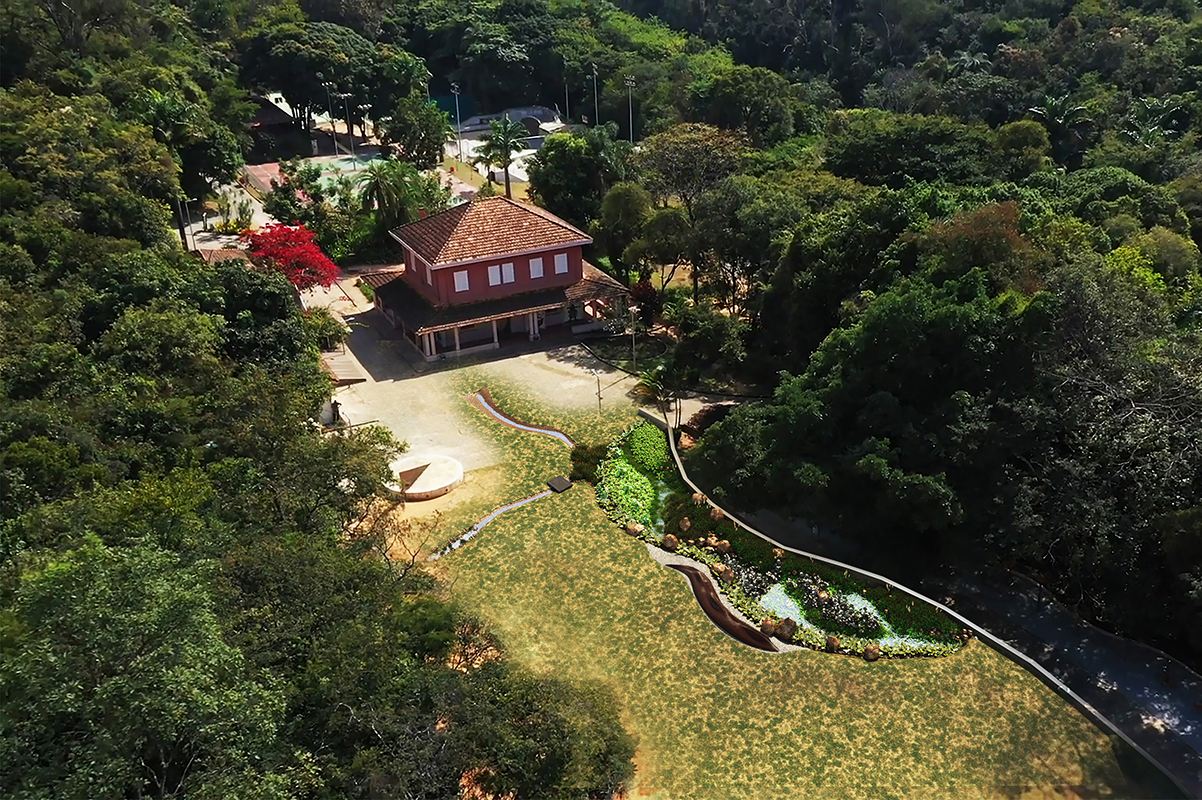
The rain garden project was created with a view to its wide replication. The city hall of Belo Horizonte, within its Pluriannual Governmental Action Plan (PPAG Portuguese acronym) has as a goal the implementation of 30 rain gardens in the municipality by 2025.
Sustainability and Resilience
What efforts have been made to reduce the carbon footprint of the initiative?
In the rain garden, the superficial runoff will enter in a centralized manner in bio-valets, and in a distributed manner from the direct contributing area to the garden. However, it was discussed that to further improve the water absorption performance during extreme rainfall events, the water outlet will be either through the infiltration or the overflow, seeking to reduce the impact caused by the intense volume.
How have the anticipated impacts of climate change been considered?
The initiative has shown itself as a case of success involving the usage of pluvial runoff for the reuse of rainwater. In Brazil the cities of Campinas and Londrina are carrying out similar projects in the construction of rain garden structures. Moreover, considering the cities that make up the metropolitan region of Belo Horizonte, this project is a successful example that can be studied and replicated in other locations. The municipality of Contagem, which is part of this metropolitan region of Belo Horizonte, has shown commitment to the creation of rain gardens.
What processes does the initiative include for it to be considerate in its use of soils and other natural resources?
This is a 100% sustainable project and involves no carbon emissions. Its creation aims to filter pollutants with the use of plants.
Monitoring, Maintenance, and Management
How has the initiative been designed and implemented so that long-term needs for management and maintenance are reduced and can be met?
INTERACT-Bio has the understanding that it is possible to perform integrated action on biodiversity, the creation of more projects like this would make great changes in the social-environmental structure of the planet. Rain gardens have the capacity to be an intelligent and sustainable alternative, with wide availability for replication in urban regions with climatic aspects similar to Belo Horizonte.
The project aims precisely at the reuse of rainwater, in order to contribute to biodiversity. This type of work manages to unite the need to contain the impact caused by storms and at the same time use the water for ecological purposes
What protocols are in place to facilitate monitoring of results?
According to ICLEI experts, rain gardens are designed to sustain themselves. Therefore, chemical fertilization of the garden is not necessary, with the exception of organic fertilization, which can eventually be done with worm humus. Regarding water quality, the monitoring aims to evaluate the reduction of diffuse pollution, with reduction of pollution loads. For this, it is important to monitor the inflow and outflow of the green infrastructure device. In addition, during monitoring, the professionals are instructed to reuse the pruning to make a cover of leaves, branches and roots inside the garden, this will ensure protection of the superficial layer and soil moisture for the plants. This cover, called burlap, will, over time, ensure that weed growth is reduced.
How has the initiative been enhanced in response to monitoring of results?
To contribute to the reduction of rainwater runoff, the implementation of rain gardens allows the water to be filtered by the vegetation and the filter of stones and sand, and absorbed by the soil. The rain garden was designed to prevent soil erosion at its edges and, internally, in the horizontal routing of water. One of its main functions is to phytoremediate pollutants carried by surface runoff of rainwater. phytoremediation – a technique that uses the ability to absorb contaminants by integrating microorganisms present in the roots of plants to help reduce soil and water pollution. Thus, the plants used in this project were designed to improve the quality of water through; When implemented on a large scale, rain gardens retain some of the rainfall runoff, contribute to reduced flood risk, improve water and soil quality, and promote local biodiversity.